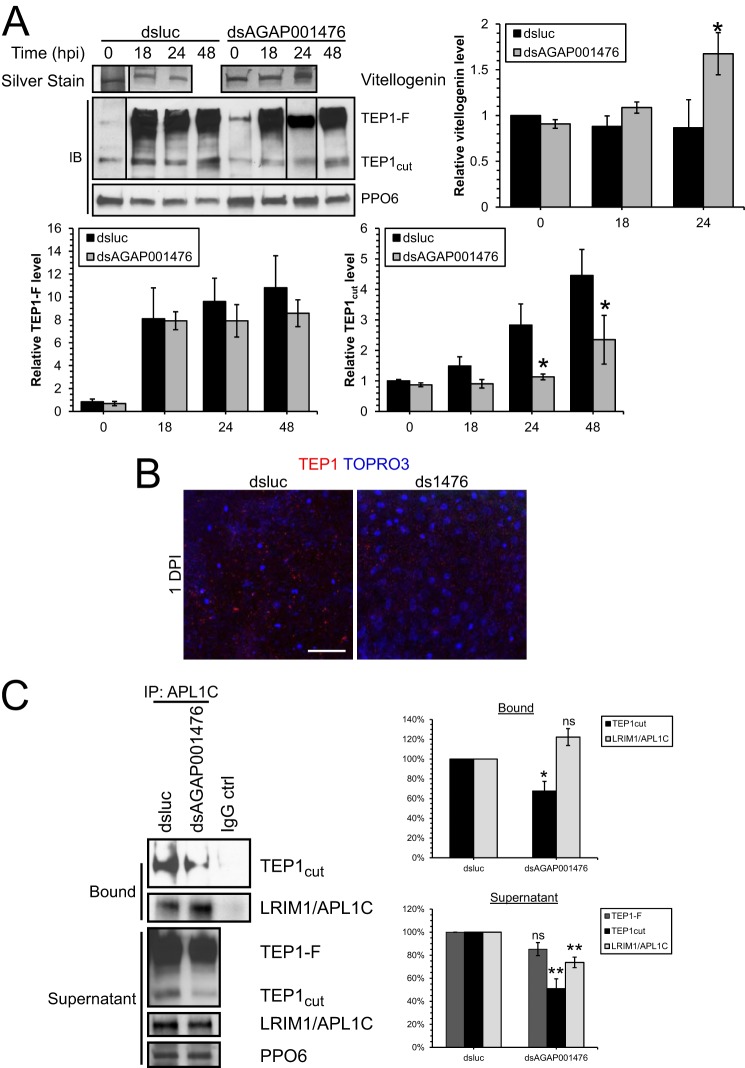
FIGURE 6.
The TEP1-LRIM1-APL1C complex was reduced in dsAGAP001476 mosquitoes at 1 dpi. A, Western blot (IB) analysis and silver staining of hemolymph collected from mosquitoes treated with dsluc or dsAGAP001476 at 0, 18, 24, and 48 hpi. More TEP1 (both TEP1-F and TEP1cut) was detected in the hemolymph during Plasmodium infection, but TEP1cut was induced to a lesser extent in dsAGAP001476 mosquitoes at 24 and 48 hpi. The induction of Vg protein level in hemolymph during Plasmodium infection was potentiated at 24 hpi in dsAGAP001476 mosquitoes. Each lane represents hemolymph collected from 10 mosquitoes. PPO6 serves as loading control. Data in the bar chart represent means ± S.E. of the mean compiled from three independent experiments. B, immunofluorescence staining of TEP1 in midguts of dsluc or dsAGAP001476 mosquitoes. There was less TEP1 attached onto the midgut epithelium in dsAGAP001476 mosquitoes at 1 dpi. C, TEP1 and LRIM1-APL1C complex was immunoprecipitated from hemolymph collected at 24 hpi using rabbit anti-APL1C antibody to assess the amount of TEP1-LRIM1-APL1C complex. Bound and unbound (supernatant) fractions were resolved by SDS-PAGE. A 30% reduction in TEP1cut-LRIM1-APL1C complex was observed from dsAGAP001476 hemolymph, in addition to a 50% reduction in TEP1cut in the supernatant. Both SDS-PAGE and immunofluorescence had been performed in three independent experiments. (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 by two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni's multiple comparisons test, or t test.) ns, no statistical significance. Scale bar, 50 μm.