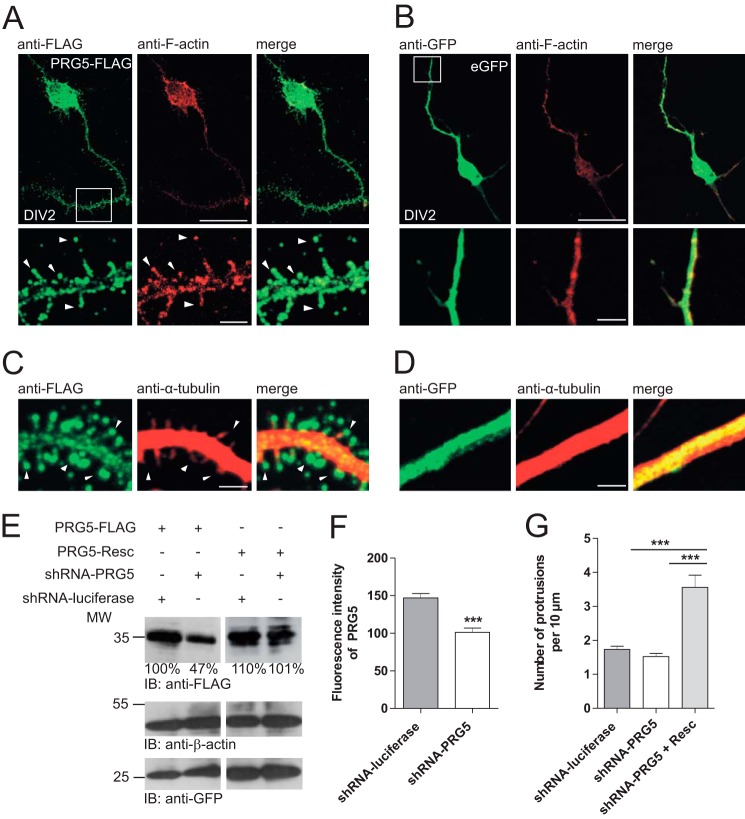
FIGURE 2.
PRG5 induces spine-like structures in immature hippocampal neurons. A, hippocampal primary neurons transfected with PRG5-FLAG (left, green) and co-immunostained with anti-F-actin (middle, red). Magnification (white frame, lower images) shows that PRG5 overexpression induces spine-like structures along neurites. Arrowheads indicate PRG5 expression in the bulbous head. B, eGFP overexpressing hippocampal neurons have the typical morphology of immature neurons. There is no spine formation along the neurites. C and D, magnification of neurites from neurons transfected with PRG5-FLAG or eGFP and co-stained with anti-FLAG (green) and anti-α-tubulin (red). White arrowheads indicate heads of different spine-like structures induced by PRG5 overexpression in comparison with eGFP-transfected cells (C). Scale bars for the upper images in A and B represent 10 μm and for the magnified sections (lower images) in A and B, and 4 μm for C and D, respectively. E, verification of PRG5 shRNA and shRNA-resistant PRG5 construct by Western blot. PRG5-FLAG was reduced when compared with controls or with PRG5 shRNA-resistant protein levels. Ratios below the Western blot bands refer to densitometry measurements of the gray intensity of these bands in relation to the control band. Anti-β-actin was used as loading control and for normalization. Anti-GFP shows transfection efficiency. IB, immunoblot. F, quantification of shRNA-PRG5 efficiency. The shRNA-PRG5 (n = 94) expression reduced endogenous PRG5 expression more than one-third when compared with control (n = 112). G, PRG5 knockdown did not affect the numbers of protrusions/filopodia in immature neurons. Primary neurons were transfected with shRNA-PRG5 or controls at DIV1 and morphologically analyzed at DIV2. Numbers of protrusions/filopodia per 10 μm in immature neurons were counted. When co-transfected with PRG5, rescue plasmid (Resc.) protrusion/filopodia drastically increased. The mutations are silent so that the rescue plasmid is comparable with PRG5 overexpression. ***, p ≤ 0.0001.