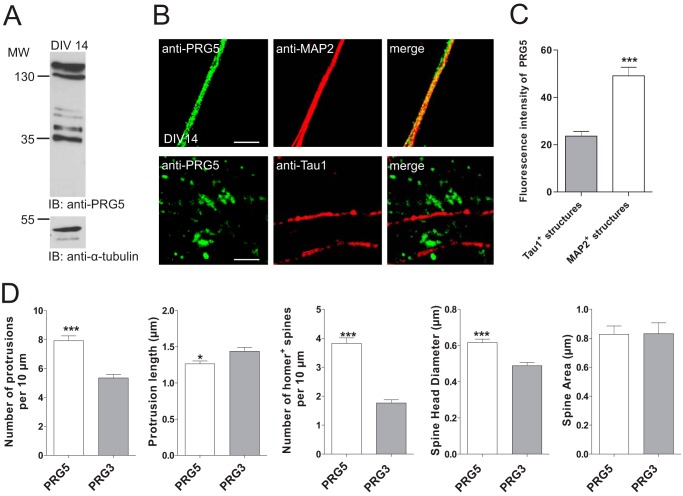
FIGURE 4.
PRG5 contributes to regulation of spine density and morphology in mature hippocampal neurons. A, Western blot analysis of membrane protein lysates from primary neurons at DIV14 shows endogenous membrane expression of PRG5. As loading control α-tubulin was used. IB, immunoblot. B, confocal images of dendritic and axonal structures from hippocampal neurons (DIV14) stained with anti-PRG5 (green) and anti-MAP2 (red, dendrites) or anti-Tau1 (red, axons) revealed a clear co-localization of PRG5 and MAP2 compared with Tau1. Scale bars, 10 μm. C, analyses of the PRG5 abundance on MAP2- and Tau1-positive structures measured by fluorescence signal intensity. Fluorescence intensity of PRG5 in MAP2-positive structures (n = 12) is significantly higher compared with the one in Tau1-positive structures (n = 69) (p ≤0.0001). D, morphology analyses in mature primary neurons transfected either with PRG5-FLAG or PRG3-FLAG 1 to 2 days after transfection. Determination of the numbers of protrusions, number of Homer-positive spines, and the spine head diameter revealed a significant increase compared with PRG3 control. *, 0.01 ≤ p ≥ 0.05, and ***, 0.001 ≤ p ≥ 0.01.