FIGURE 8.
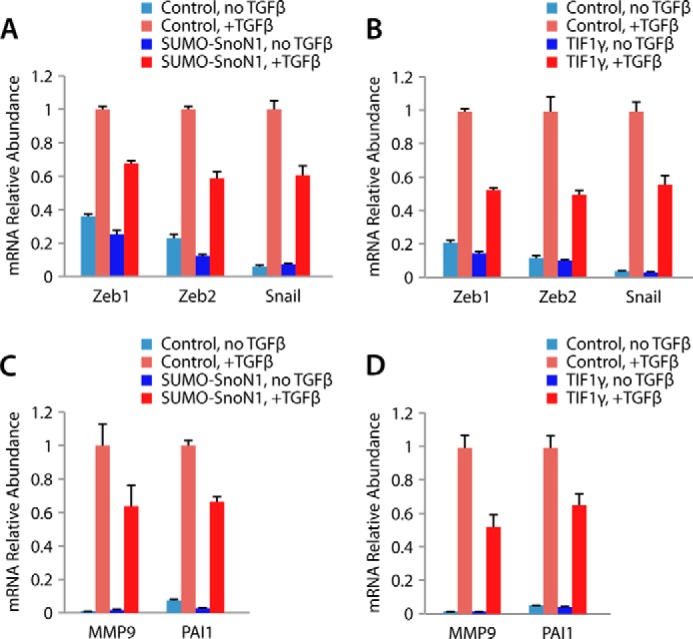
TIF1γ-SnoN sumoylation suppresses TGFβ-induced gene expression in EMT. A, quantitative RT-PCR analysis of mRNA extracted from NMuMG cells transfected with a vector control or a SUMO-SnoN1 expressing plasmid that were left untreated or incubated with 100 pm TGFβ for 24 h to measure the abundance of the mRNA of Zeb1, Zeb2, snail, and GAPDH, with the latter serving as the internal control for normalization. The mean mRNA abundance is presented relative to the expression of the plus TGFβ control, together with the mean ± S.E. from four independent experiments. SUMO-SnoN1 significantly suppressed the expression of Zeb1, Zeb2, and snail in TGFβ-treated NMuMG cells (ANOVA, p < 0.001). B, quantitative RT-PCR analysis of mRNA from NMuMG cells transfected with a vector control or a plasmid encoding FLAG-TIF1γ that were analyzed as described in A. TIF1γ significantly suppressed the expression of Zeb1, Zeb2, and snail in TGFβ-treated NMuMG cells (ANOVA, p < 0.001). C, quantitative RT-PCR analysis of MMP9 and PAI-1 as described in A. SUMO-SnoN1 suppressed the expression of MMP9 and PAI-1 in TGFβ-treated NMuMG cells (ANOVA, p < 0.05). D, quantitative RT-PCR analysis of MMP9 and PAI-1 as described in B. TIF1γ suppressed the expression of MMP9 and PAI-1 in TGFβ-treated NMuMG cells (ANOVA, p < 0.001).
