Figure 1.
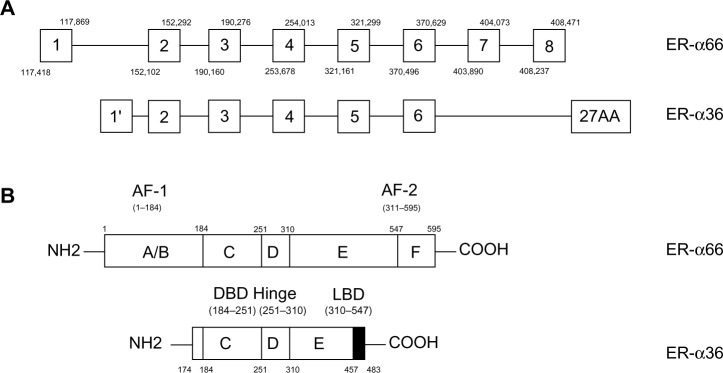
Structure of ER-α66 and ER-α36.
Notes: (A) Transcription of ER-α36 initiates from a previously unidentified promoter in the first intron of ER-α66. We labeled the first exon of ER-α36 as “1” to distinguish it. Besides, ER-α36 has an extra, unique 27-amino-acid sequence at C-terminus which may broaden ligand-binding spectrum of ER-α36. (B) Compared to the protein structure of ER-α66, ER-α36 lacks both transactivation domains of AF-1 and AF-2 and retains DBD, Hinge, and LBD of ER-α66. Therefore, ER-α36 functions as a powerful competitor of ER-α66.
Abbreviations: AF-1, activation function 1; AF-2, activation function 2; DBD, DNA binding domain; ER-α36, estrogen receptor-alpha36; ER-α66, estrogen receptor-alpha66; LBD, ligand binding domain.
