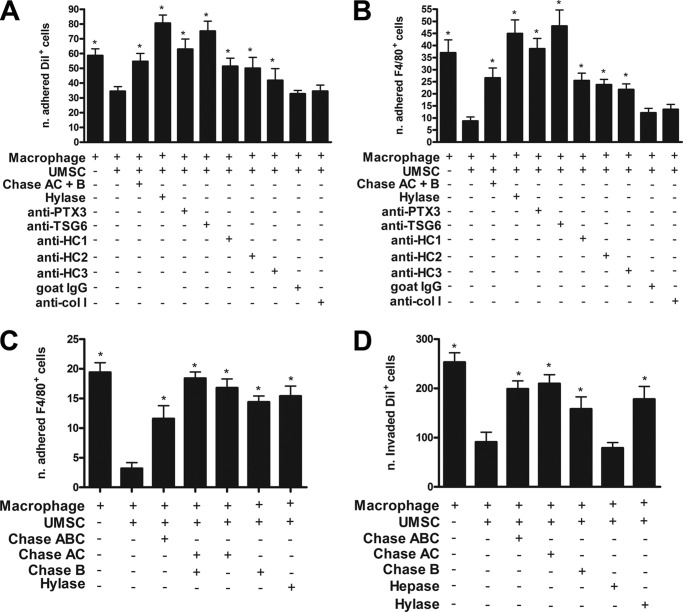
FIGURE 3.
UMSCs inhibit the adhesion and migration/invasion of inflammatory cells. The ability of the UMSCs to modulate immune cells was evaluated using a co-culture assay between UMSCs and inflammatory cells. A and B, inflammatory cells were labeled with DiI and seeded over UMSCs previously treated or not with Chase AC+B or Hylase or over UMSCs in the presence of antibodies. The numbers of adhered DiI+ cells (A) and F4/80+ cells (B) were counted. C, potential requisite of cell-cell contact between the UMSCs and the inflammatory cells was evaluated. UMSCs were seeded in a transwell insert with a 0.44-μm pore and treated or not with Chase ABC, Chase AC, Chase B, or Hylase. Thereafter, inflammatory cells were placed in the bottom chamber, and the numbers of adhered F4/80+ cells were counted. D, UMSCs were treated or not with Chase ABC, Chase AC, Chase B, Hepase, Hylase, or HylaseS. Inflammatory cells labeled with DiI were seeded in a transwell insert with a 3-μm pore. 10% FBS was placed in the bottom chamber as a stimulus to invasion. The numbers of DiI+ cells that invaded into the lower chamber were counted. * < 0.05 compared with UMSCs plus macrophages.