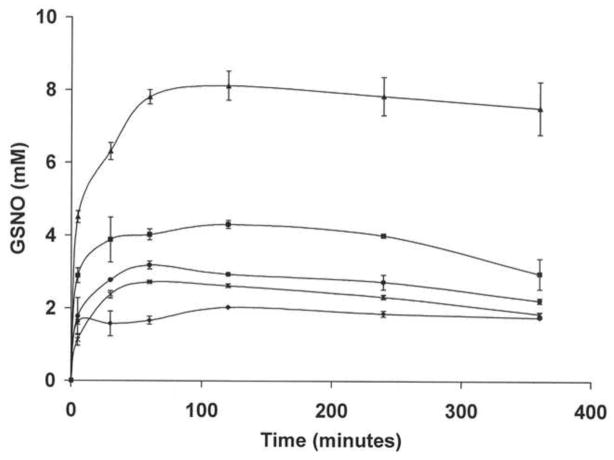
Figure 3. Time course of GSNO production from a mixture of nanoparticles and GSH.
NO-np (*), SNO-np (●), NAC-SNO-np-1 (◆), NAC-SNO-np-2 (■), and NAC-SNO-np-3 (▲) (20 mg/ml) were incubated with GSH (20 mM) in 0.5 mM DTPA/PBS, pH 7.4, at room temperature. Aliquots were taken at time intervals, 50x diluted and analyzed by RPHPLC as described in methods. GSNO concentrations were calculated from the peak areas. Values are the averages of duplicate experiments. In spite of using the same amount of nitrite, NAC-SNO-np-2 formed more GSNO and at a higher rate than NO-np and SNO-np. The rate and amount of GSNO formed from the three formulations of NAC-SNO-np were proportional to the amount of nitrite used in the preparation of these particles. These results demonstrate the highest S-nitrosation efficiency of NAC-SNO-np.