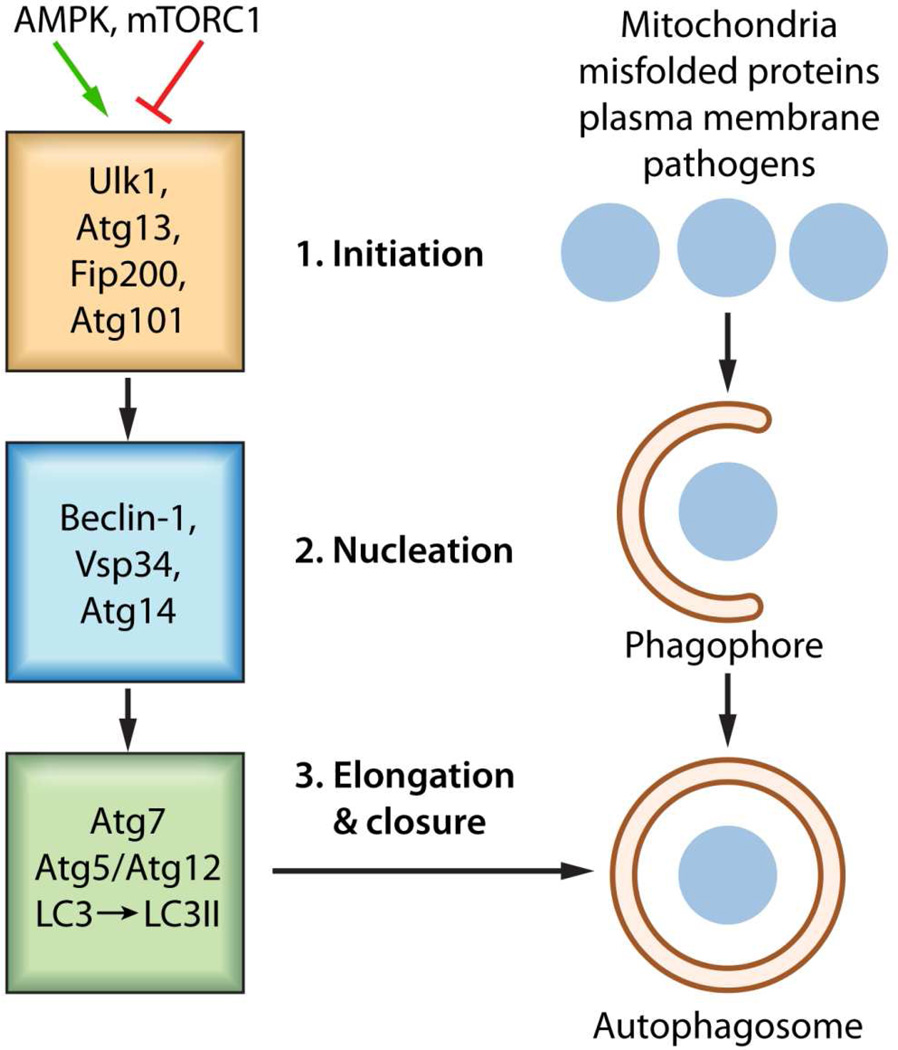
Figure 1. Basic autophagic processes.
The stages of autophagosome formation are illustrated. Autophagosome formation, an evolutionarily conserved process utilizes an Initiation stage (1), a Nucleation stage (2) as well as an Elongation and Closure stage (3), ultimately the degradation of autophagosomal content proceeds through fusion of autophagosome with lysosome in an autolysosome in a degradation stage. 1. The mTOR complex (shown as mTORC1) represses autophagy when amino acids energy and growth factors are abundant through the inhibition of ULK1 activity. Upon energy deprivation the Initiation Stage commences through the stimulation of Ulk1 kinase activity and phosphorylation of its substrates Atg13 and FIP100. Rapamycin removes the mTOR mediated inhibition of autophagy 2. During the nucleation stage, the generation of PtdIns3P by the Vsp34 allows for the recruitment of additional factors. The functional relationship between the individual components of the initiation stage and nucleation stage is unclear. 3. The expansion and subsequent closure of the autophagosome depends on the Atg5/Atg12 conjugate system which facilitates the lipidation of LC3 to LC3II by phosphatidylethanolamine (PE).