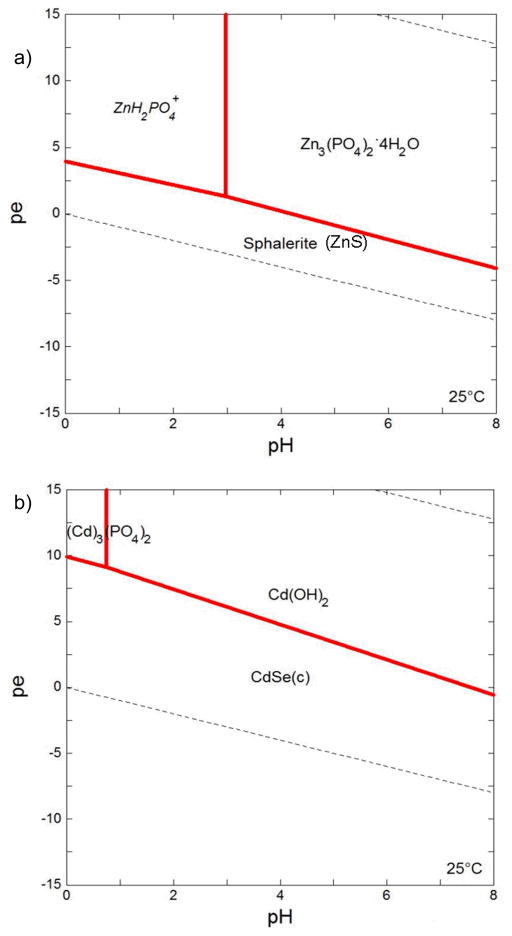
Figure 7.
pε-pH diagrams for (a) ZnS and (b) CdSe under simulated gastric conditions at 25°C. Diagrams were produced using Geochemist’s Workbench v 3.0 (Bethke, 1998). Stability constants for Se, S and Zn species were from the data table for the program. Solubility products and stability constants for cadmium species were taken from Bard et al. (1985), Hankare et. al. (2006), and Stumm and Morgan (1996). The concentrations of ionic species reflected those in the simulated gastric fluids. Total amounts of Cd (10−2.1 mole) and Zn (10−7.7 mole) were based on concentrations measured by ICP-OES (Figures 2 and 3). As Se and Cd are present in 1:1 stoichiometry, total Se is equal to total Cd. Concentration of S was set at 10−5 M. (italics = dissolved species; (c) = cubic)