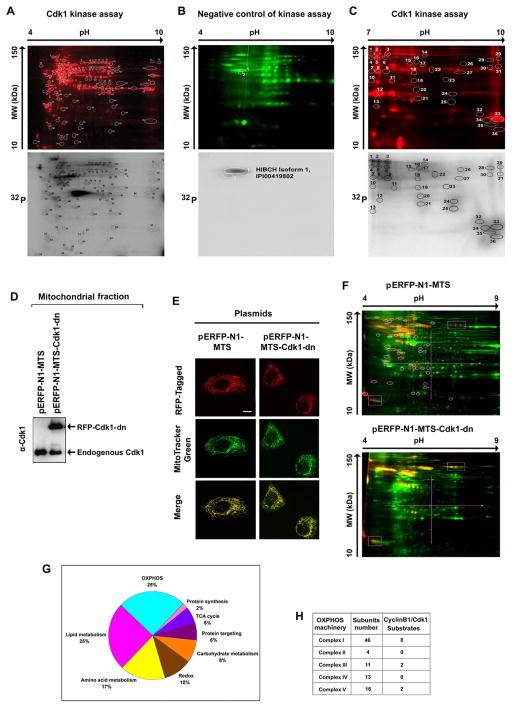
Figure 2. Potential Mitochondrial Substrates of Cdk1.
(A) Mitochondrial (Mi) proteins (1 mg) isolated from G0/G1 cells were incubated with commercial Cdk1 in the presence of [γ-32P] ATP, of which 50 μg was separated by 2-D gel electrophoresis (pH 4–9) after labeled with Cy5 (upper panel). The phosphorylated spots were detected by autoradiography (lower panel) and the circled spots were extracted and identified by mass spectrometry and the potential Cdk1 -phosphorylated Mi proteins are listed in Table S1.
(B) A negative control of (A) with the absence of commercial Cdk1 and presence of the Cdk1 inhibitor RO-3306.
(C) Cdk1-Mi target proteins detected with the same Cdk1 kinase assay as (A) with electrophoresis in the range pH 7–10.
(D) Immunoblotting analysis of Cdk1 in Mi fractions isolated from cells transfected with mitochondria-targeted dominate negative mutant Cdk1 and empty vectors.
(E) Representative images of mitochondria-targeted (MTS) Cdk1-wt-RFP, Cdk1-dn-RFP and empty vector MTS-RFP.
(F) Mi proteins extracted from G2/M-peaked cells transfected with mitochondria-targeted empty vector (pERFP-N1-MTS, upper panel) or mutant Cdk1 (pERFP-N1-MTS-Cdk-dn, lower panel) were labeled with Cy5 (green), separated by 2-D gel and phosphorylated proteins were stained with Pro-Q Diamond dye (red). Spots absent in the Mi profile of cells with mitochondria-targeted mutant Cdk1 compared with the vector control transfectants (circled) were extracted and analyzed by mass spectrometry. The potential Cdk1 Mi targets detected by these experiments were listed in Table S3.
(G) Summary of potential Cdk1-targeted mitochondrial proteins detected by in vitro (A–C) and in vivo (E–F) Cdk1 kinase assays.
(H) Distribution of potential MiCdk1 targets in the subunits of complexes. See also Tables S1–S4.