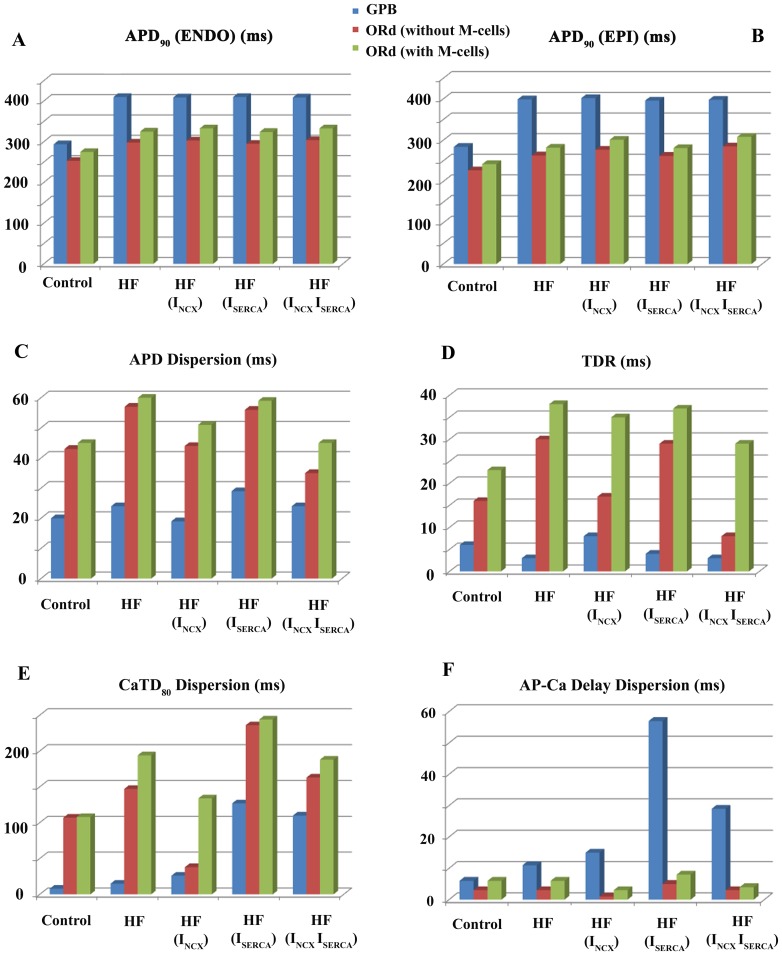
Figure 3. Biomarkers in normal, homogeneous and heterogeneous remodeling failing conditions with GPB, ORd (without M cells), and ORd (with M cells) models.
Electrophysiological properties measured in a one dimensional transmural ventricular strand under different pathological conditions. The ventricular strands were composed by 82 endocardial and 83 epicardial cells. All simulations were conducted using Grandi et al. (GPB) action potential model [34] (blue bars), O'Hara et al. [35] model (ORd) without M-cells (red bars) and ORd model with M cells (green bars). The cases considered were: normal conditions (Control), electrical homogeneous heart failure remodeling (HF), electrical heterogeneous heart failure remodeling on INCX (HF INCX), electrical heterogeneous heart failure remodeling on ISERCA (HF ISERCA), and electrical heterogeneous heart failure remodeling on INCX and ISERCA simultaneously (HF INCXISERCA). The mean action potential duration (APD) along the endocardial (panel A) and epicardial (panel B) strand was measured at 90% repolarization. Dispersion in APD (panel C) was measured along the entire strand as the difference between maximal and minimal APD, avoiding first and last fifteen cells. Transmural dispersion of repolarization (TDR) (panel D) was measured by adding the APD to the time of depolarization of each cell. The calcium transient duration (CaTD80) (panel E) was measured from the upstroke to 80% of calcium transient amplitude, dispersion was assessed as in APD. AP-Ca delay (panel F) was measured as the difference between the upstroke in AP and in calcium transient along the entire strand, dispersion was also evaluated as in APD (see Methods section for details).