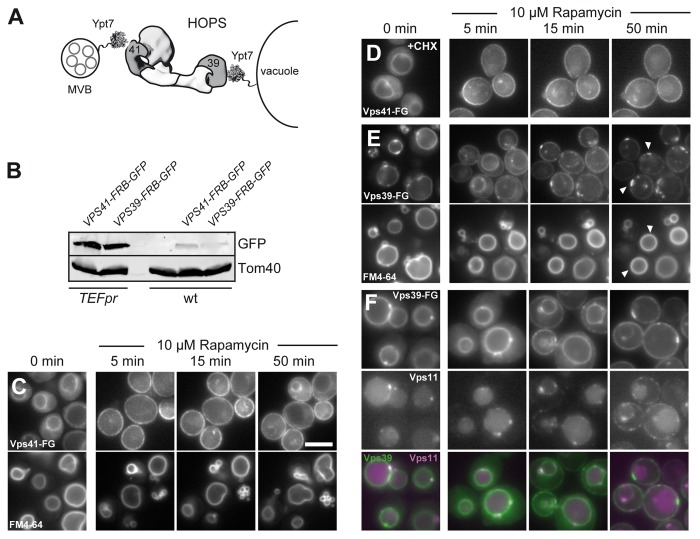
Figure 2. Dynamic relocalization of the HOPS-specific Vps39 and Vps41. (A) Model of HOPS function between membranes. Ypt7 is present on multivesicular bodies (MVBs) and vacuoles and binds to HOPS via Vps41 and Vps39. HOPS is shown as a structural model based on the electron microscopy structure.3 (B) Expression levels of Vps41 and Vps39 in wild-type and overexpression condition was analyzed by loading similar amounts of cell lysate onto SDS-PAGE gels. Proteins were detected after western blotting using anti-GFP to detect Vps41 and Vps39, and anti-Tom40 antibody as loading control. (C-E) Dynamic relocalization of the two Rab-specific HOPS subunits Vps41 and Vps39. The indicated subunits were placed under the control of the TEF1 promoter and tagged with FRB-GFP and analyzed as in Figure 1. In (C), FM4–64 staining was done in Vps41-FRB-GFP expressing cells to analyze vacuole morphology during the time course. In (D), 10 µg/ml of the translation inhibitor cyclohexamide was added before rapamycin addition. The same result was obtained with 50 µg/ml cyclohexamide (not shown). (E) Vps39-FRB-GFP was analyzed, and vacuolar contacts to the plasma membrane are indicated by arrows. The bottom panel shows vacuolar straining as in (C). In (F), Vps11 was tagged with mCherry in the strain carrying Vps39-FRB-GFP, and analysis was done as in (E). Size bar is 5 µm.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.