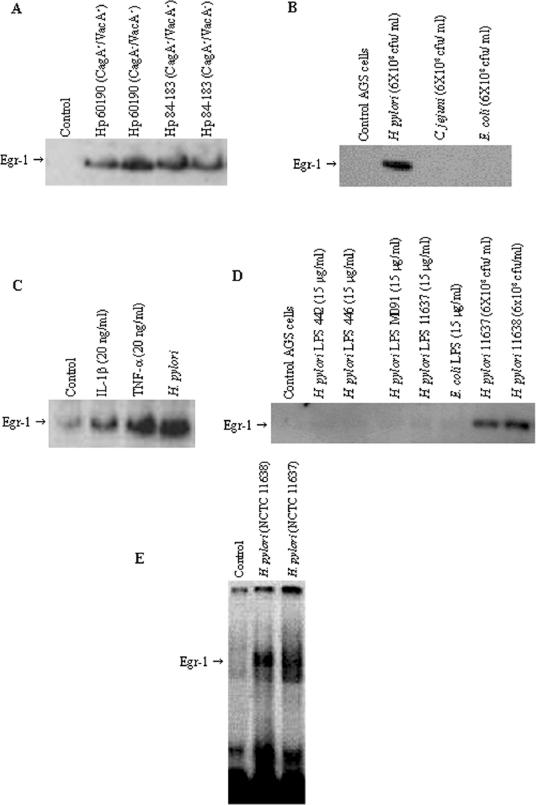
FIG. 2.
(A) Effect of H. pylori isogenic mutant strains on Egr-1 expression. AGS cells were incubated for 2 h with CagA+ toxigenic H. pylori strain 60190, its CagA− toxigenic isogenic mutant, CagA+ toxigenic strain 84-183, and its CagA+ VacA− nontoxigenic isogenic mutant. (B) Effect of other bacteria on Egr-1 expression. C. jejuni. E. coli, and H. pylori (NCTC 11638) were cocultured (6 × 108 CFU/ml) with subconfluent AGS cells for 2 h. A Western blot analysis of Egr-1 protein was performed on total cell extracts (50 μg of protein/lane). (C) IL-1β and TNF-α activate Egr-1 expression in AGS cells. AGS cells were treated with IL-1β (20 ng/ml), TNF-α (20 ng/ml), or H. pylori NCTC 11638 (6 × 108 CFU/ml) for 2 h. (D) Effect of H. pylori LPS on Egr-1 expression. AGS cells were incubated with H. pylori LPS (from strains 442, 446, M091, and NCTC 11637) or E. coli LPS at a concentration of 15 μg/ml or with live H. pylori bacteria (NCTC 11637 and NCTC 11638) at 6 × 108 CFU/ml for 2 h. A Western blot analysis of Egr-1 protein was performed on total cell extracts (50 μg of protein/lane). (E) EMSA analysis of Egr-1 activation by H. pylori in AGS cells. AGS cells were incubated with a freshly harvested suspension of H. pylori NCTC 11638 or NCTC 11637 (6 × 108 CFU/ml) for 2 h, and nuclear extracts were prepared and analyzed for Egr-1 DNA binding by EMSA. Control, untreated AGS cells are shown in lane 1. Representative gels of three independent experiments with similar results are shown.