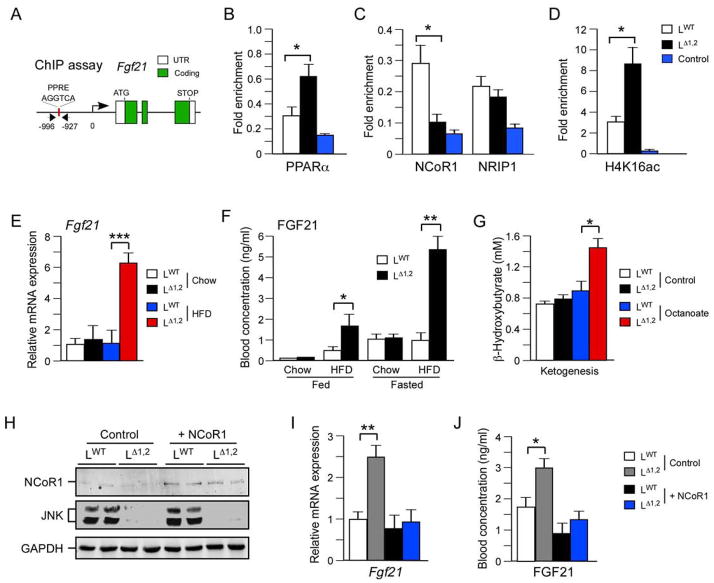
Figure 6. The FGF21 pathway is repressed by JNK.
(A–D) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays were performed using liver isolated from overnight fasted LWT and LΔ1,2 mice with antibodies to non-immune immunoglobulin (Control), PPARα, NCoR1, NRIP1, and acetyl-lysine16 histone H4 (H4K16ac). The fold enrichment of a fragment of the Fgf21 promoter with a PPRE site was measured by quantitative PCR analysis (mean ± SEM; n = 6; p < 0.05).
(E) The hepatic expression of Fgf21 mRNA in overnight fasted mice was examined by quantitative RT-PCR analysis (mean ± SEM; n = 8; ***, p < 0.001).
(F) The concentration of FGF21 in the blood of chow-fed and HFD-fed LWT and LΔ1,2 mice was measured by ELISA. Blood was collected from mice fed ad libitum or fasted overnight (mean ± SEM; n=6 *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01).
(G) Ketone body production was measured in overnight-fasted LWT and LΔ1,2 mice challenged (6 h) without (Control) and with Octanoate (mean ± SEM; n = 5; *, p < 0.05).
(H–J) NCoR1 or GFP (Control) were expressed in the liver of HFD-fed (4 wks.) LWT and LΔ1,2 mice using recombinant adenovirus vectors (10 ~ 16 days). The mice were fasted overnight and hepatic expression of NCoR1 and GAPDH were examined by immunoblot analysis (H). The amount of Fgf21 mRNA was measured by quantitative RT-PCR analysis (I) and the concentration of FGF21 in the blood was measured by ELISA (J). The data presented are the mean ± SEM; n = 6; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.
See also Figure S7.