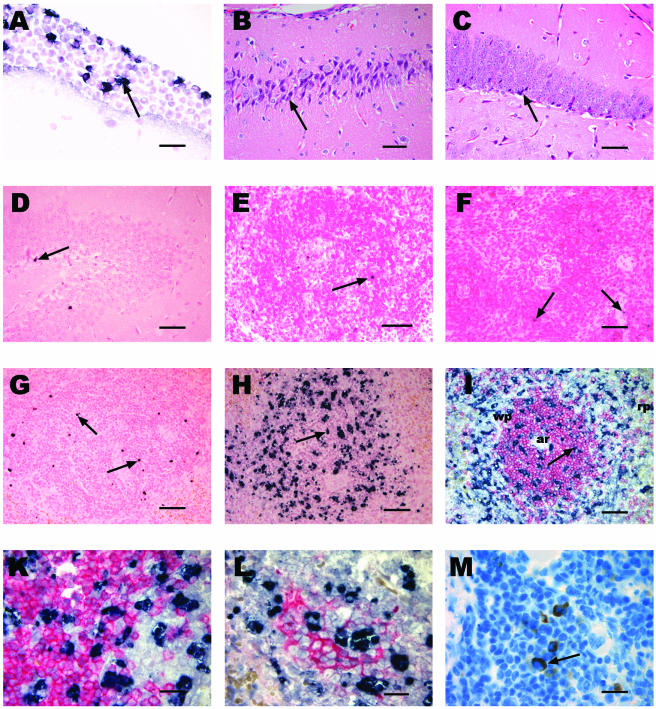
FIG. 2.
Histology and immunohistochemistry of the brain and spleen in experimental S. pneumoniae meningitis in Bcl-2-deficient mice and controls. (A) In situ tailing of the brain showing meningeal inflammation in a Bcl-2-deficient mouse with apoptotic PML (arrow). Bar, 20 μm. (B and C) Hematoxylin and eosin staining showing necrotic neuronal damage (arrow) in the CA3 region of the hippocampus of a Bcl-2-deficient mouse (B) and in the dentate gyrus of a Bcl-2-deficient mouse (C). (D) In situ tailing of the brain showing an apoptotic neuron (arrow) in the dentate gyrus of a Bcl-2-deficient mouse. (E and F) In situ tailing of the spleen showing few apoptotic lymphocytes (arrow) in a heterozygous control mouse (E) and in a Bcl-2-deficient mouse (F) into which saline was injected. (G and H) In situ tailing of the spleens of a wild-type mouse (G) with few apoptotic lymphocytes (arrow) and a Bcl-2-deficient mouse (H) showing a markedly increased number of apoptotic lymphocytes (arrow) 36 h after intracerebral infection with S. pneumoniae. Bars in panels B to H, 50 μm. (I) Double staining of spleen slices with in situ tailing (black) and CD3 (red) showing apoptotic lymphocytes (arrow) mainly in the white pulp (wp) within and outside T-cell regions. Note the arteriole (ar) in the center of the T-cell region located in the periarteriolar lymphatic sheath. The red pulp (rp) is visible at the edge and does not contain as many apoptotic cells. Bar, 50 μm. (K) Higher magnification showing that there are no cells that show clear double staining with in situ tailing (black) and CD3 (red) due to the shrunken cytoplasm of apoptotic cells. (L) Double staining with in situ tailing (black) and CD8 (red) showing apoptotic lymphocytes within a cytotoxic T-cell cluster and also outside this area. (M) Bcl-2 staining (arrow) in splenic lymphocytes. Bars in panels K to M, 20 μm.