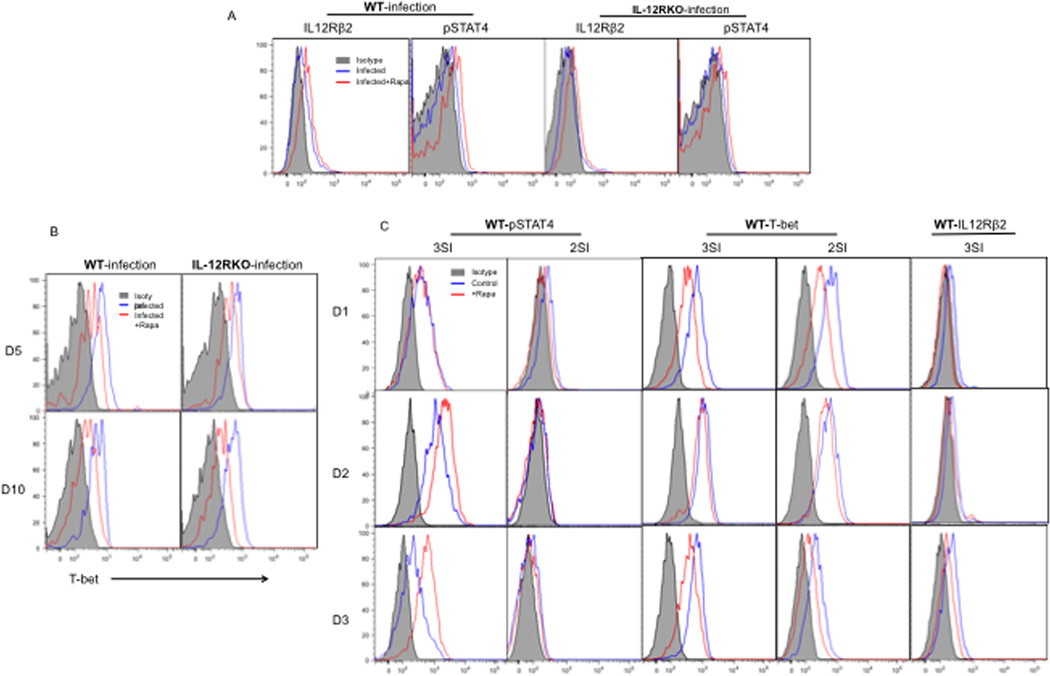
Figure 6. Rapamycin enhances IL-12 signaling in early infection and consistently inhibits T-bet expression.
Naïve WT or IL-12RKO OT-I cells were transferred into recipient B6 mice, which were infected with VV-OVA the next day. High doses of rapamycin were administered daily between D-1 and D10 post VV-OVA infection. OT-I cells in spleens were examined at days 5 (A) and 10 after infection (B). The results are representative of 5 mice per group, and similar data were obtained in two separate experiments. C. Sorted WT OT-I cells were stimulated with 3SI (antigen+B7+IL-12) or 2SI (antigen+B7) in the presence or absence of rapamycin as we previously reported 10. Programmed CTLs were examined at day 3 post-stimulation. The T-bet was examined on effector CTLs generated in vivo (B) and in vitro (C). These are representatives of two independent experiments with similar results.