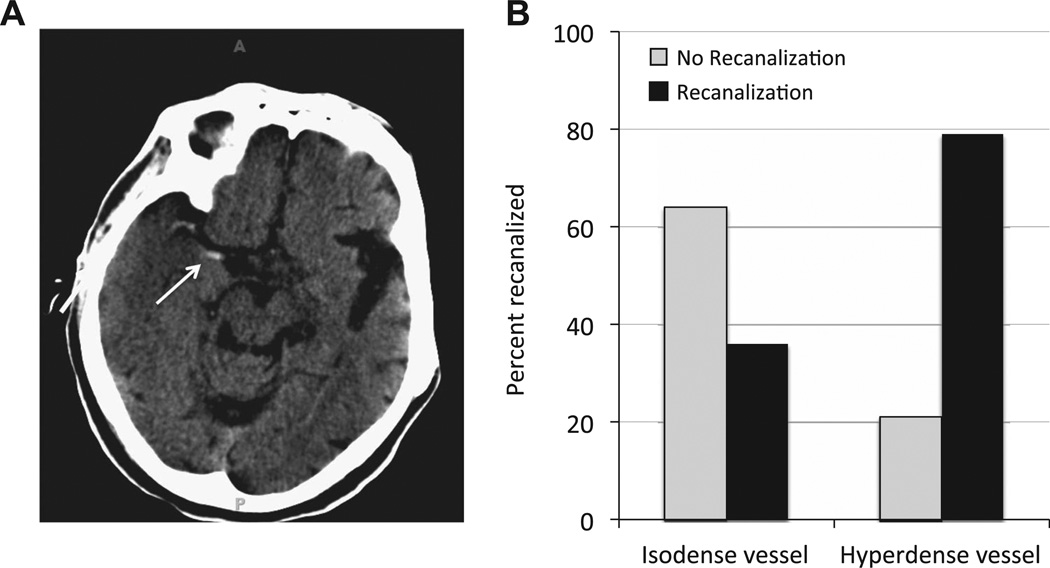
Figure 1.
(A) An example of the hypderdense vessel sign (HVS) in the right middle cerebral artery seen on non-contrast CT. The arrow indicates the clot seen in the proximal portion of the middle cerebral artery, but additional clot can also be seen as hyperdensity near the M1–M2 junction on this scan. (B) Patients that exhibited the HVS had a 79% likelihood of successful recanalization (right side). In contrast, when the HVS was not observed (isodense vessel; left side), mechanical recanalization was much more likely to fail. Only 36% of patients without the HVS experienced successful recanalization.