Figure 5.
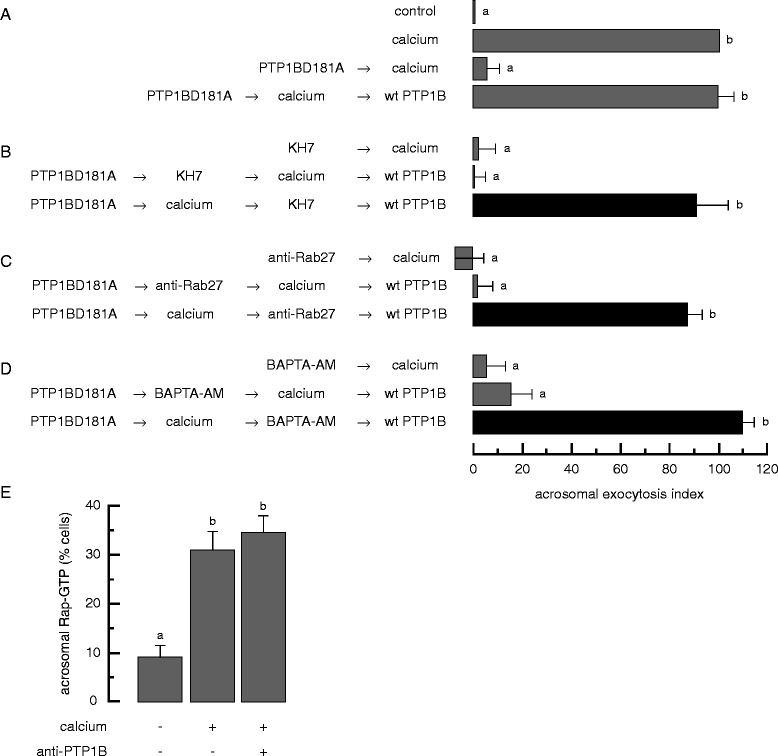
Inhibition of sperm PTP1B does not interfere with intracellular calcium mobilization from the acrosome: results obtained with the reversible pair substrate trapping mutant PTP1BD181A (inhibitor 1)/wild type PTP1B (rescue inhibitor 1). SLO-permeabilized spermatozoa were loaded with 300 nM PTP1BD181A for 8 min at 37°C to block the signaling pathway where PTP1B is required. The AR was subsequently initiated by adding 0.5 mM CaCl2. After 8 min incubation at 37°C to allow exocytosis to proceed to the PTP1B-sensitive step, sperm were treated with 10 μM KH7 (B), 7 nM anti-Rab27 antibodies (C), or 10 μM BAPTA-AM (D), and incubated for an additional 8 min at 37°C. Last, we added 27 nM wild type PTP1B (wt PTP1B) to rescue the mutant PTP1B block and incubated as before (black bars). We run several controls in parallel (grey bars): background AR in the absence of any stimulation (control), AR stimulated by 0.5 mM CaCl2 (calcium); inhibition by 10 μM KH7, 7 nM anti-Rab27 antibodies, and 10 μM BAPTA-AM; rescue of PTP1BD181A by wild type PTP1B; and the inhibitory effect of the blockers when present throughout the experiment (PTP1BD181A → calcium → KH7/anti-Rab27/BAPTA-AM → wt PTP1B). Sperm were fixed and AR was measured by FITC-PSA binding as described under Methods. The data represent the mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments. (E) SLO-permeabilized sperm were treated with 3.3 nM anti-PTP1B antibodies. The AR was initiated with 0.5 mM CaCl2. Incubations were for 15 min at 37°C after each addition. Samples were processed for Rap-GTP immunodetection as described under Methods. Shown is the percentage of cells immunodecorated in the acrosomal region with the anti-GST antibodies, representing active Rap. The data represent the mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments. Different letters indicate statistical significance (P < 0.001).
