Figure 2.
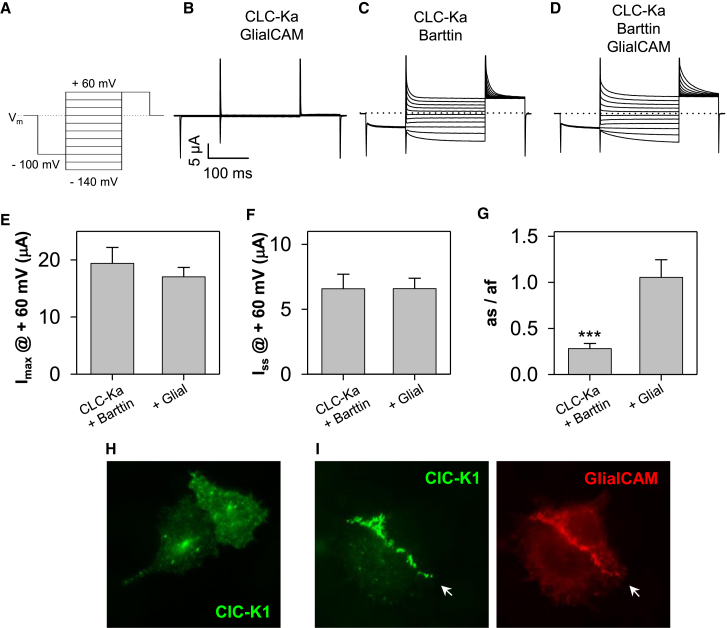
hCLC-Ka/Barttin mediated currents are modulated by GlialCAM. (A) Pulse protocol. (B–D) Typical currents from oocytes injected with CLC-Ka and GlialCAM (B), CLC-Ka and Barttin (C), or CLC-Ka, Barttin, and GlialCAM (D). Amount of cRNA for each construct was kept constant in the different co-injections. In (C) and (D) same scale bars as in (B). From the tail current after the –140 mV prepulse, the initial current (Imax), shown in (E) and the steady state current (Iss), shown in (F) were determined. A double exponential fit to this tail current yielded time constants and coefficients of the two exponential components (see Methods). Fast and slow time constants were for CLC-Ka/Barttin 43 ± 11 ms and 6.8 ± 1 ms, for CLC-Ka/Barttin/GlialCAM 36 ± 1 ms and 8.7 ± 0.3 ms, respectively (n = 10), i.e., not significantly different. (G) Ratio of slow (as) and fast coefficient (af) of the double exponential: the weight of the slow component is significantly increased by GlialCAM. (∗∗∗p < 0.001, Student’s t-test), values are mean ± SE. (H–I) Cellular distribution of CLC-K1 in HeLa cells. Barttin-CLC-K1 alone is located uniformly in the plasma membrane and intracellularly (H) whereas GlialCAM leads to CLC-K1/barttin localization in regions of cell-cell contacts (I, arrow). To see this figure in color, go online.