Fig. 1.
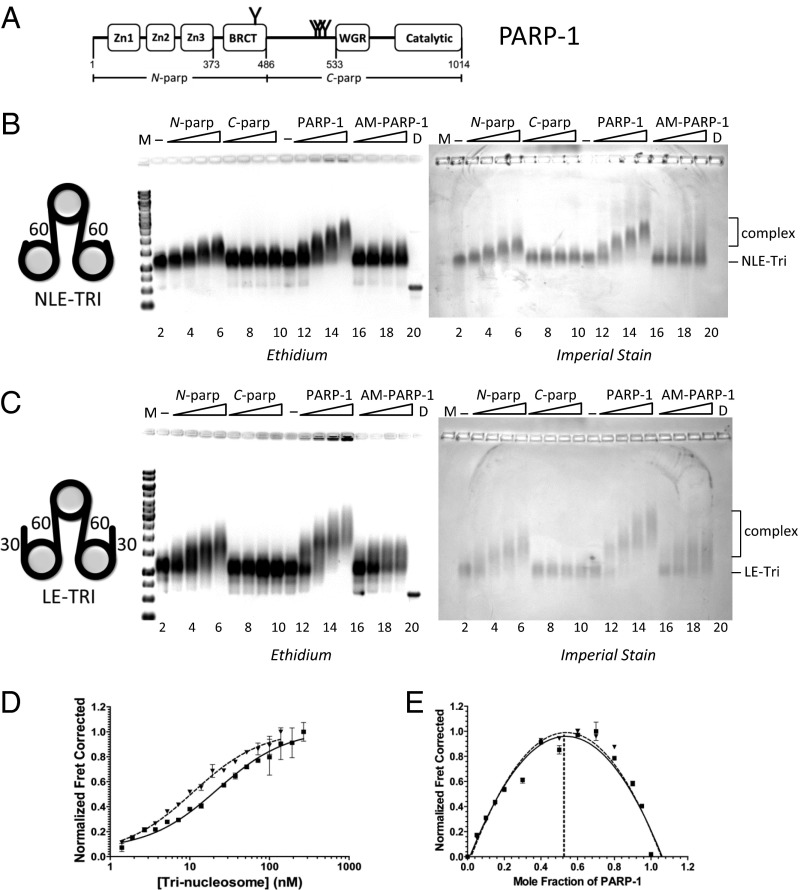
High-affinity interactions of PARP-1 with chromatin do not require exposed DNA ends. (A) PARP-1 domain structure. Commonly described automodification sites are indicated by Y. The N-parp and C-parp constructs used in this study are indicated. BRCT, BRCA1 C terminus. (B and C) EMSA of trinucleosomes without free linker DNA (NLE-Tri, B) or with 30-bp linker DNA extensions (LE-Tri, C) bound to various PARP-1 constructs. Trinucleosomes (lanes 2 and 11) were incubated with increasing amounts of N-parp (lanes 3–6), C-parp (lanes 7–10), PARP-1 (lanes 12–15), or AM–PARP-1 (lanes 16–19). Gels were stained as indicated. D, DNA; M, marker (521 bp in B and 621 bp in C). (D) Representative HI-FI FRET curves of PARP-1 with LE-Tri and NLE-Tri. Error bars are from duplicates within a single experiment. The solid line indicates LE-Tri, and the dashed line indicates NLE-Tri. The Kd values from these and similar experiments are listed in Table 1. (E) Job plots for stoichiometry for samples shown in D. LE-Tri (■, solid line) and NLE-Tri (▲, dashed line) are shown.