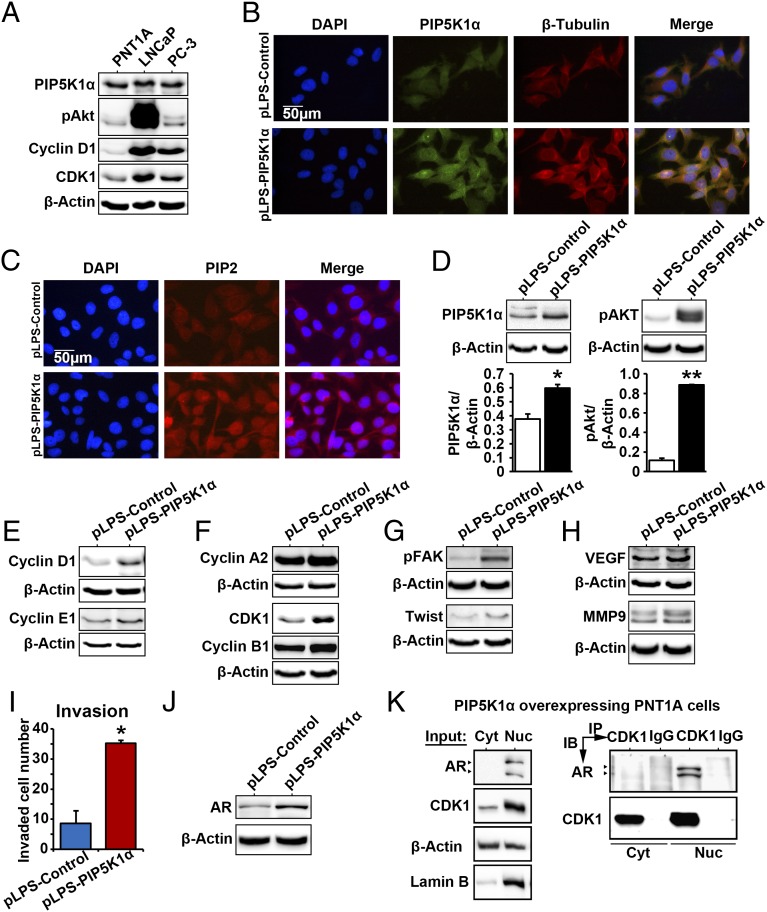
Fig. 4.
PIP5K1α overexpression promotes malignant phenotype in nonmalignant epithelial PNT1A cells via AKT/AR/CDK1 pathways. (A) Immunoblots show the expression of PIP5K1α, phosphorylated AKT, cyclin D1, and CDK1 in a panel of PCa cell lines including PNT1A, LNCaP, and PC-3. (B) Effect of PIP5K1α overexpression on the morphology of PNT1A cells. Representative immune-fluorescent images show the overexpression of PIP5K1α and its colocalization with β-tubulin. DAPI was used to stain the nucleus of cells. The scale bar is indicated. (C) Representative images of the immunofluorescent cells overexpressing PIP5K1α or control vector, stained with PIP2 antibody. (D) Immunoblots show the effect of PIP5K1α overexpression on PNT1A cells. The mean expression of PIP5K1α in cells transfected with pLPS-EGFP control vector was 7.42, and the mean value in cells transfected with pLPS-PIP5K1α was 10.96 (difference = 3.54; 95% CI 5.89–16.02; P = 0.047). The mean expression of AKT in cell transfected with pLPS-EGFP control vector was 3.78, and the mean value in cells transfected with pLPS-PIP5K1α was 29.02 (difference = 25.24; 95% CI 21.67–36.37; P = 0.021). Data are presented as the average of three independent experiments (±SD). *P < 0.05. **P < 0.01. (E) Immunoblots show the effect of overexpression of PIP5K1α on cyclin D1, cyclin E1, and (F) cyclin A2, CDK1, and cyclin B1 or (G and H) phosphorylated FAK, Twist, VEGF, and MMP9 in PNT1A cells. (I) The number of invaded cells is indicated. Data are presented as an average of triplicates (±SD). *P = 0.014. (J) Immunoblots show the expression of AR in PNT1A cells overexpressing PIP5K1α or control vector. (K) Cytoplasmic (Cyt) and nuclear (Nuc) fractions were separated from PNT1A cells overexpressing PIP5K1α. Cells were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) assay as shown (Right). Antibody to CDK1 was used to pull down the immunocomplexes, and antibody to IgG was used as a negative control. Antibodies against AR or CDK1 were used for immunoblot analysis (IB). The cell lysates from cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions were used as “Input” controls as indicated (Left). Blotting of actin served as loading control, and antibody against lamin B was used as a control for the nuclear fraction.