Table 3. Homodimerization of Canonical Amino Acids for Investigating Side-Chain Influence on Catalytic Activity.
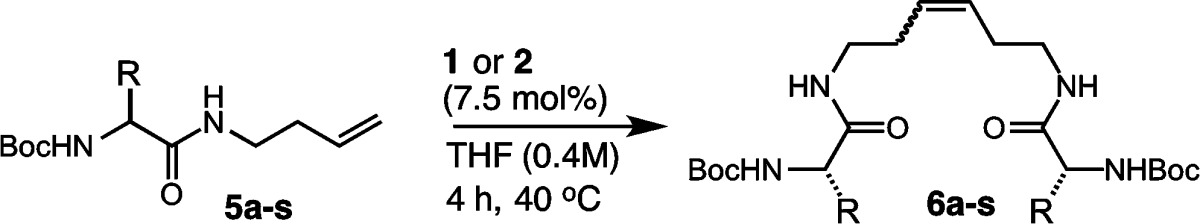
| yielda (%) |
Z selectivityb (%) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | amino acid | product | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 1 | valine (5a) | 6a | 74 | 71 | 90 | 94 |
| 2 | isoleucine (5b) | 6b | 68 | 72 | 88 | 92 |
| 3 | leucine (5c) | 6c | 70 | 71 | 88 | 91 |
| 4 | phenylalanine (5d) | 6d | 73 | 75 | 89 | 93 |
| 5 | glycine (5e) | 6e | <10 | <10 | n.d. | n.d. |
| 6 | proline (5f) | 6f | <10 | <5 | n.d. | n.d. |
| 7 | tryptophan (5g) | 6g | 66 | 64 | 85 | 90 |
| 8 | histidine (5h) | 6h | <5 | <5 | n.d. | n.d. |
| 9 | serine (5i) | 6i | 72 | 70 | 84 | 90 |
| 10 | threonine (5j) | 6i | 73 | 70 | 88 | 92 |
| 11 | tyrosine (5k) | 6k | 64 | 68 | 87 | 90 |
| 12 | methionine (51) | 61 | <5 | <10 | n.d. | n.d. |
| 13 | cysteine (5m)c | 6m | 55 | 53 | 87 | 92 |
| 14 | aspartic acid (5n)d | 6n | 61 | 60 | 87 | 90 |
| 15 | glutamic acid (5o)d | 6o | 74 | 71 | 88 | 91 |
| 16 | asparagine (5p)c | 6p | 70 | 71 | 88 | 91 |
| 17 | glutamine (5q)c | 6q | 74 | 74 | 88 | 91 |
| 18 | lysine (5r)e | 6r | 78 | 81 | 81 | 89 |
| 19 | arginine (5s)e | 6s | 34 | 33 | 81 | 89 |
Isolated yields.
Determined by 1H or 13C NMR spectroscopy.
Side chain protected with a trityl group.
Side chain protected as the t-butyl ester.
Side chain protected as the t-butyl carbamate.
Side chain protected with 2,2,4,6,7-pentamethyldihydrobenzofuran-5-sulfonyl (Pbf).
