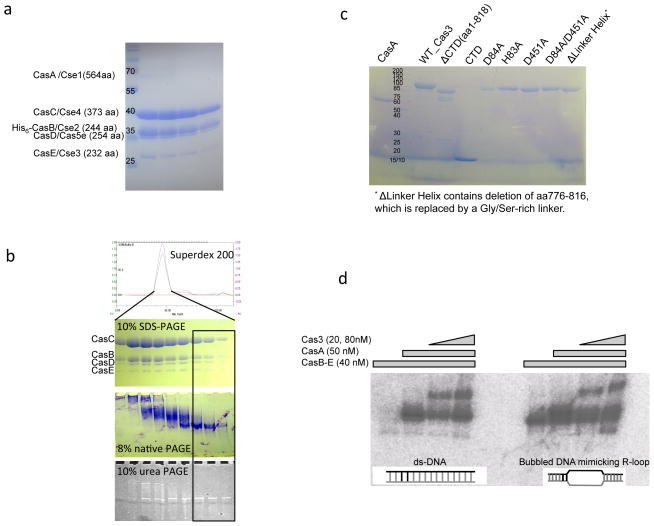
Figure 5. Reconstitution of Cas3-Cascade/R-loop interaction in vitro from purified components.
(a) Cascade (CasA-E) purification. SDS-PAGE of the Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) peak containing the co-expressed T. fusca Cascade. The protein identity in each band was verified by mass spectrometry. The expected stoichiometry of CasA-E and crRNA is 1:2:6:1:1:1. CasA is significantly sub-stoichiometric. (b) CasB-E Cascade sub-complex purification. Protein and RNA qualities were checked on the SEC elusion profile, 10% SDS-PAGE, 6% native PAGE, and 10% urea-PAGE. Note that even though the subunit stoichiometry was roughly the same across the SEC peak, the boxed half of the SEC peak contained monomeric CasB-E/crRNA complex, whereas the front half of the peak contained various aggregated forms. (c) Quality of CasA and Cas3 wild type and mutant proteins used in the biochemical studies on SDS-PAGE. (d) Reconstitution of Cascade/ R-loop and Cas3/Cascade/R-loop complexes. Substrate in the EMSA is either a perfectly base-paired ds-DNA or a bubbled DNA substrate mimicking an R-loop opened at the spacer region. R-loop formation with the former substrate requires CasA present. Cas3 interacts with the programmed Cascade robustly only when CasA is present.