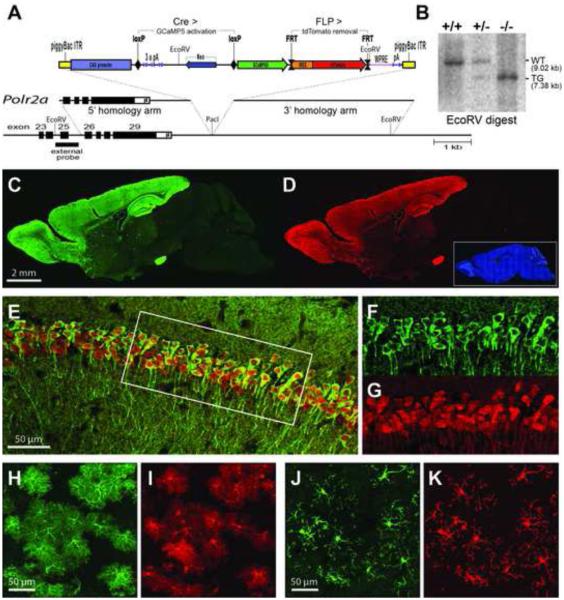
Figure 1. Generation and Characterization PC::G5-tdT.
(A) A schematic diagram of the PC::G5-tdT allele. Both 5’ and 3’ homologies of the targeting vector are shown in relation to the endogenous Polr2a gene encoding the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II. The reporter component of the targeting vector is shown on top. The CAG promoter drives GCaMP5G and IRES-tdTomato expression following Cre-mediated excision of the STOP (3x pA) cassette. The IRES-tdTomato reporter can be independently removed with FLP recombinase. ITR, inverted repeats, pA, polyadenylation signal; WPRE, Woodchuck hepatitis posttranscriptional regulatory element. (B) Southern blot analysis of tail DNA from control (+/+), heterozygous (+/-) and homozygous (-/-) Polr2aCAG-GCaMP5G,tdTomato/CAG-GCaMP5G,tdTomato animals. DNA was digested with EcoRV and hybridized with the external probe indicated in (A). (C,D) Sagittal sections from heterozygous Emx1-IRES-Cre; PC::G5-tdT brains were stained with anti-GFP (GCaMP5G) and anti-RFP (tdTomato) antibodies and specifically imaged (C) in the green channel for GCaMP5G and (D) in the red channel for tdTomato. Blue DAPI staining is shown as an inset in (D). (E-G) Hippocampal CA1 region of CamKIIα-Cre; PC::G5-tdT heterozygous animals stained with GFP and RFP antibodies. (E) Overlay of GCaMP5G and tdTomato signals. (F,G) Details of GCaMP5G and tdTomato signals, respectively, corresponding to the area framed with the white box in (E). (H,I) Cortical astrocytes from GFAP-CreER; PC::G5-tdT animals and (J,K) cortical microglia from brains of Hoxb8-IRES-Cre; PC::G5-tdT genotype. Both astrocytes and microglia were stained as above and specifically imaged (H,J) for GCamP5G and (I,K) for tdTomato. Adult animals ranging in age from 5-8 weeks were used for immunohistochemistry in panels C-K. See also Figures S1, S2, S3 and S4.