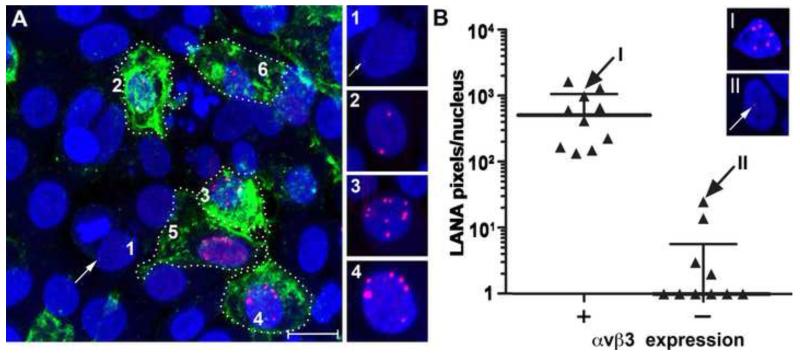
Figure 11. Ectopic expression of αVβ3 integrin renders HSG cells susceptible to KSHV infection.
HSG cells were transfected with a β3 integrin expression plasmid and subsequently infected with KSHV, as described in Methods. A) Cell surface β3 integrin was detected on live cells using mAB B3A (green). The cells were then fixed and nuclear KSHV LANA was detected using mAB LN53 (red). Fluorescent signals were sequentially enhanced using TSA 488 and TSA 594, respectively. Nuclei were counterstained with TO-PRO 3 (blue). The cell borders of a number of transfected HSG cells expressing αVβ3 are marked with a dotted line. One untransfected (αVβ3-negative) cell (#1) and five transfected (αVβ3-positive) cells are numbered (2-6). Fluorescent staining of the nuclear LANA protein is shown in the montage of individual nuclei at the right with the 488 (green) laser off. A very weak LANA fluorescent spot was detected in the untransfected cell #1 (arrow). B) LANA expression was quantitated by counting fluorescent pixels per nucleus for αVβ3 expressing and non-expressing HSG cells. αVβ3-positive cells (median = 510 pixels/nucleus); αVβ3-negative cells (median = 0 pixels/nucleus) (P=0.0001; Mann-Whitney U test). Micrographs of the cell nuclei corresponding to data points “I” (αVβ3-positive; 991 LANA pixels) and “II” (αVβ3-negative; 25 LANA pixels) are shown for comparison. Bar = 20 μM.