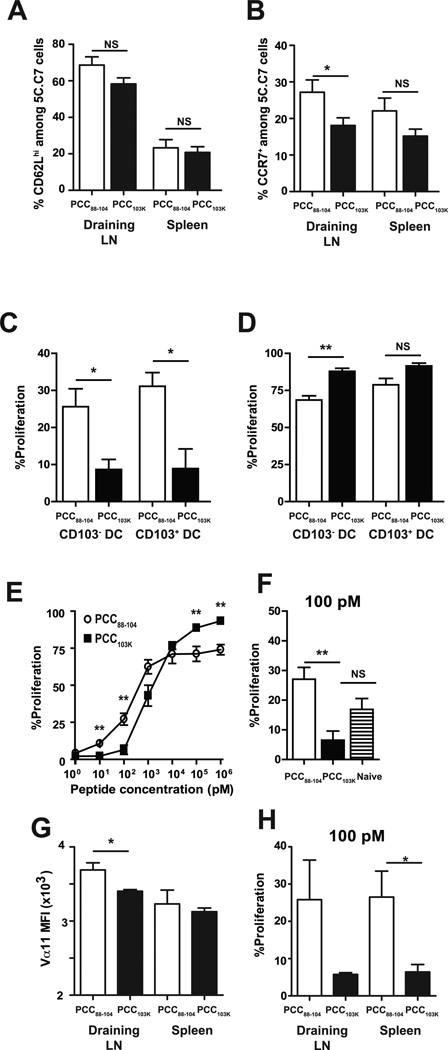
Figure 7. High stability peptide-induced Th cells fail to proliferate in response to lung DCs from infected mice.
Splenocytes from 5C.C7αβ TCR transgenic mice were adoptively transferred into congenic mice, and recipient mice were s.c. immunized with PCC88–104 or PCC103K peptides. (A) Frequency of CD62Lhi or (B) CCR7+ 5C.C7 cells in the indicated organs 7 days after immunization with indicated peptides. Means ± SEM for at least six animals are shown. (C-F) Draining LN and spleen of recipient mice were harvested 7 days after immunization. 5C.C7 cells were sorted and CFSE-labeled. (C–D) CFSE-labeled 5C.C7 day 7 effector cells were cultured without (C) or with (D) 1 µM MCC88–103 peptide and CD103+ or CD103− DCs sorted from MLNs of B10.BR mice infected with WSN-MCC88–104 influenza virus 2 days before. (E–F) CFSE-labeled 5C.C7 day 7 effector cells and (F) naïve 5C.C7 cells were cultured with purified splenic DCs from naïve mice and (E) various concentrations of MCC88–103 peptide or (F) 100 pM of MCC88–103 peptide. After 72 h, cell division was determined by flow cytometry. Frequencies of dividing CD4 T cells (Thy1.2+CFSElo) are displayed. (G) Vα11 staining MFI of 5C.C7 cells in indicated organs 7 days after immunization. (H) CFSE-labeled 5C.C7 day 7 effector cells derived from draining LN or spleen were cultured with purified splenic DCs from naïve mice and 100 pM of MCC88–103 peptide. After 72 h, cell division was determined by flow cytometry. Frequencies of dividing CD4 T cells (Thy1.2+CFSElo) are displayed. Means ± SEM for at least three animals are shown. *p ≤ 0.05, (unpaired Student t test), **p ≤ 0.01 (unpaired Student t test). Data shown are derived from at least three independent experiments (n ≥ 3 mice per group).