Figure 6.
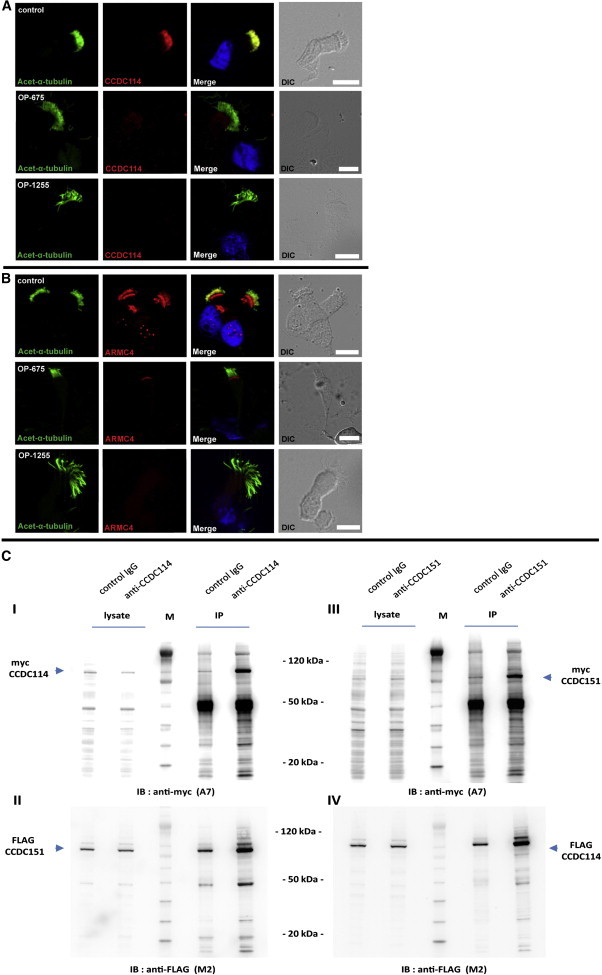
Mutations in CCDC151 Affect the Localization of ODA-Microtubule Docking-Complex-Associated Components CCDC114 and ARMC4 in Human Respiratory Cells and the ODA-Associated CCDC151 Interacts with CCDC114
(A and B) Respiratory epithelial cells from an unaffected control and PCD-affected individuals carrying CCDC151 mutations were double-labeled with antibodies directed against acetylated α-tubulin (green) and CCDC114 (A, red) or ARMC4 (B, red). CCDC114 and ARMC4 colocalize with acetylated α-tubulin along control ciliary axonemes (merge, yellow). However, in respiratory cells from individuals OP-675 and OP-1255 carrying mutations in CCDC151, CCDC114 and ARMC4 are undetectable in the ciliary axonemes. Scale bars represent 10 μm.
(C) HEK293 lysates coexpressing FLAG or myc epitope-tagged CCDC151 and CCDC114 were immunoprecipitated with either rabbit control IgG and rabbit anti-CCDC151 or anti-CCDC114 antibody. Immunoblotting with mouse anti-myc or anti-FLAG antibody demonstrates that CCDC114 immunoprecipitates CCDC151 (I, II) and CCDC151 immunoprecipitates CCDC114 (III, IV). The open reading frames of recombinant CCDC151 and CCDC114 are 595 and 670 amino acids, respectively. The observed approximate molecular weights of 85 and 100 kDa, respectively, represent additional sequence from myc- and FLAG epitope tags. Equal volumes (12 μl) of lysate and immunoprecipitate fractions were loaded on the same gel; lysate fractions represent 0.5% of total lysate (1 ml volume) and immunoprecipitate fractions represent 1/15 lysis volume (33 μl resuspension). Magic Mark protein ladder (M) was used to estimate molecular weight of recombinant CCDC151 and CCDC114.
