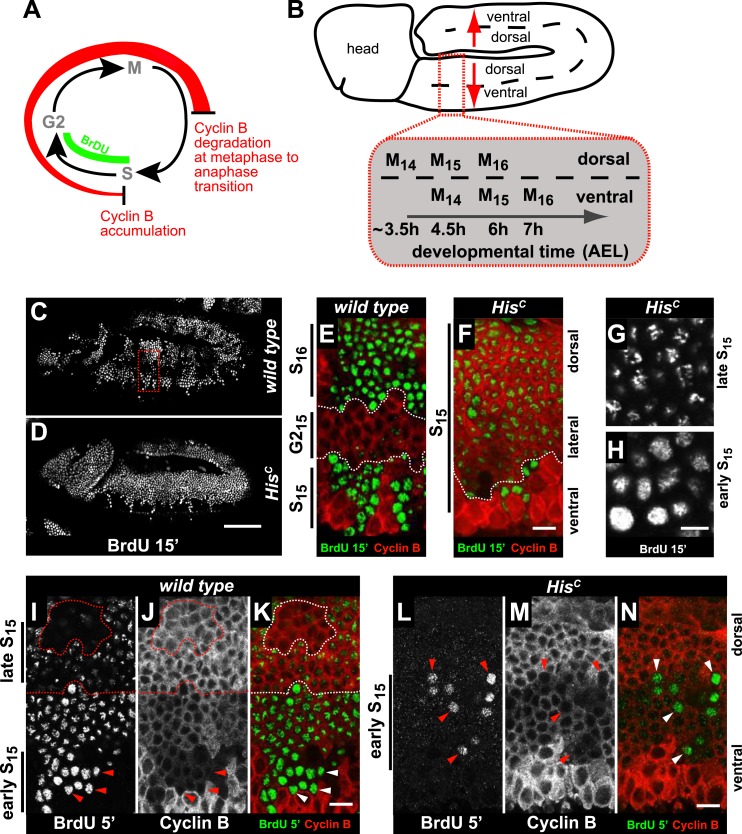
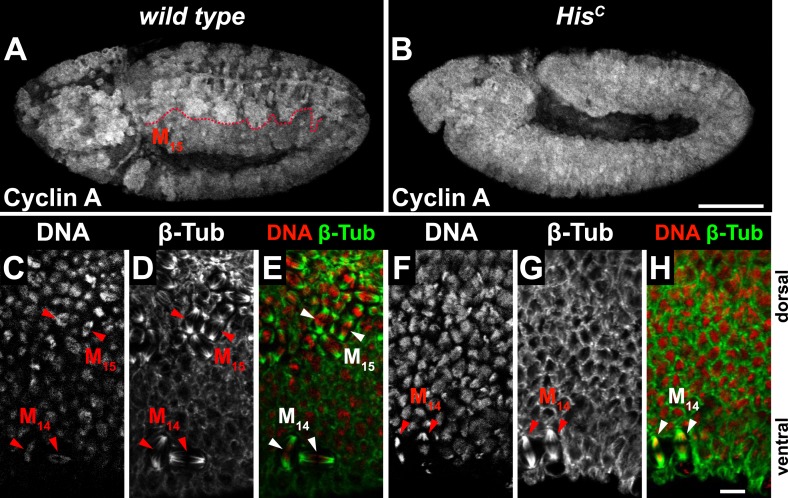
Figure 2. HisC mutant cells extend S phase and slow down DNA synthesis.
(A and B) Schematic models of Cyclin B accumulation and BrdU incorporation during the embryonic cell cycle (A) and its spatial control (B). AEL: after egg laying. (C–N) BrdU pulse labelling for 15 (C–H) or 5 min (I–N) and staining with antibodies against BrdU (green in merge) and Cyclin B (red in merge). (C and D) BrdU was detected in the epidermis of HisC mutant embryos indicating DNA replication but the pattern of replicating cells was distinct from wild type. (E and F) Magnifications of an epidermal region as shown for the wild type embryo (boxed area in C). (E) BrdU labelled wild type cells of the ventral epidermis in S15 (below dashed lines) and of the dorsal epidermis in S16 (above dashed lines). Cells in G215 were BrdU negative with high levels of Cyclin B and located in the lateral epidermis (between dashed lines). (F) In HisC mutant embryos, lateral and dorsal cells re-accumulated Cyclin B and were labelled for BrdU (above dashed line), indicating that mutant cells still replicated DNA during S15. (G and H) Punctate pattern of BrdU incorporation in cells that progressed into late S15 in the dorsal epidermis (G) and uniform incorporation pattern in cells of the ventral epidermis (H). (I–K) In wild type embryos replicating cells in early (ventral, below dashed line) and late S15 (dorsal, above dashed line) were detected after a 5 min BrdU labelling pulse. Some patches of dorsal cells completed S15 and did not incorporate BrdU (encircled). (L–N) In HisC mutant embryos BrdU was detected after a 5 min BrdU labelling pulse only in ventral cells that were in early S phase as indicated by low levels of Cyclin B (arrowheads). Dorsal up (E–N), scale bars: 100 µm (C and D), 10 µm (E–N).