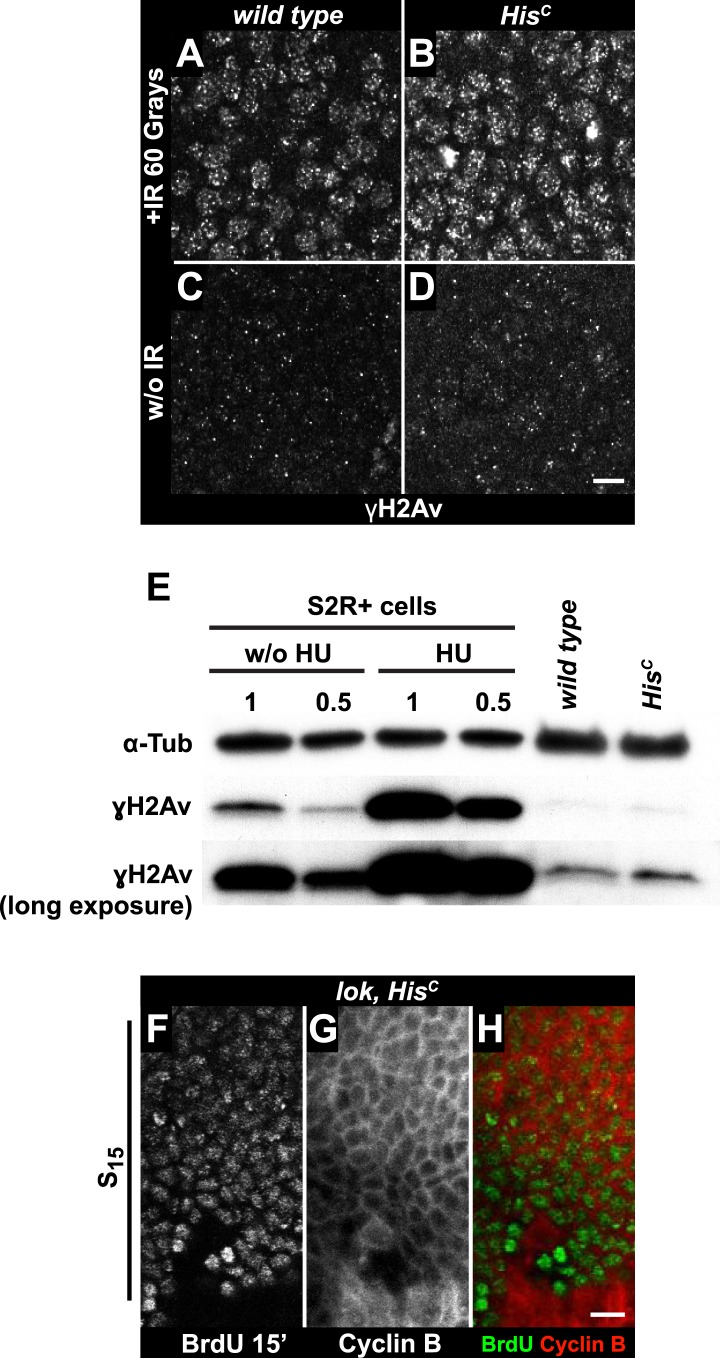
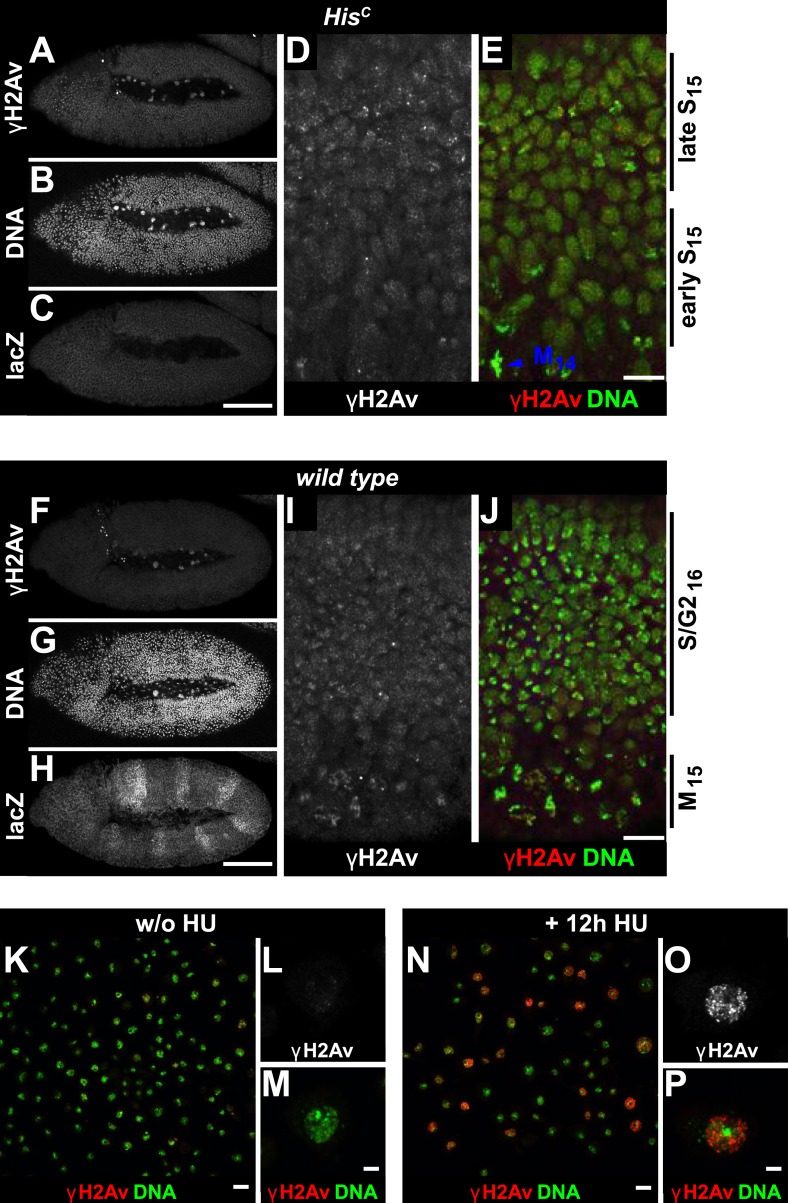
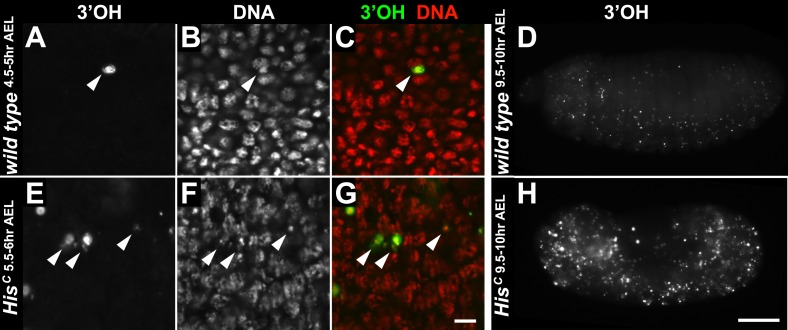
Figure 4. The cell cycle arrest of HisC mutant cells does not depend on the ATM/Chk2 DNA damage checkpoint.
(A and B) Wild type and HisC mutant cells responded to ionizing irradiation (IR) by phosphorylation of the variant histone H2Av, detected by a phosphospecific antibody against H2Av (γH2Av). (C and D) Without irradiation, HisC mutant cells did not show elevated γH2Av staining compared to wild type, indicating that mutant cells did not accumulate DNA damage. (E) Western blot for γH2Av using untreated (w/o HU) and HU-treated (HU) S2R+ cells as controls (two dilutions, 1 and 0.5) as well as HisC mutant embryos and wild type embryos at 5.5–6.5 hr AEL. α-Tubulin (α-Tub) was used as a loading control. HU treatment results in a significant increase of γH2Av, which was not observed in HisC mutant embryos. (F–H) BrdU pulse labelling for 15 min and staining with antibodies against BrdU and Cyclin B. lok, HisC double mutant embryos showed a similar phenotype as HisC mutant embryos (see Figure 1F). Dorsal up in (F–H), scale bars: 10 µm.