Figure 5. TRIM9 inhibits NIK-mediated non-canonical NF-κB processing.
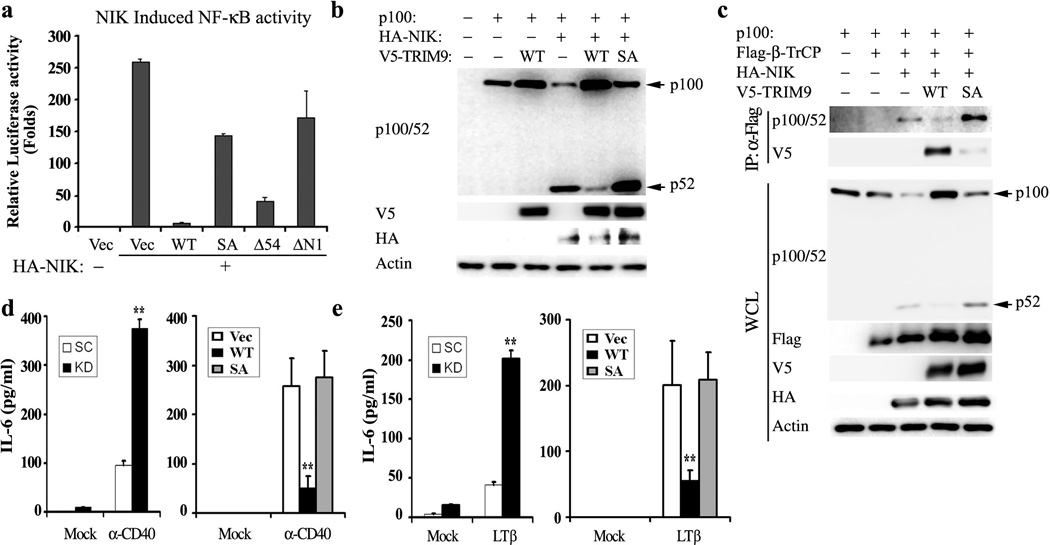
(a) At 24h post transfection with NF-κB reporter plasmid, NIK, and HA-TRIM9 WT or its mutants, HEK293T cells were used for dual-luciferase assay. (b and c) At 48h post transfection with p100, HA-NIK and TRIM9 WT or SA mutant, HEK293T cell lysates were used for IB with the indicated antibodies. (c) At 48h post transfection with p100, Flag-β-TrCP, HA-NIK, TRIM9 WT or SA mutant, HEK293T cell lysates were used for IP with anti-Flag and IB with anti-p100/52 or anti-TRIM9 antibody. WCL were used for IB with the indicated antibodies. Arrows indicate the precursor p100 protein and the processed p52 protein. (d and e) Upon depletion of TRIM9 expression (left panel) or expression of TRIM9 WT or SA mutant (right panel), human Raji B cells were treated with α -CD40 (d) and A549 epithelial cells were treated with LT β (e) for 24h and their supernatants were subjected to IL-6 ELISA. The mean ± s.d. is shown:**p < 0.01.The data are representative of three independent experiments.
