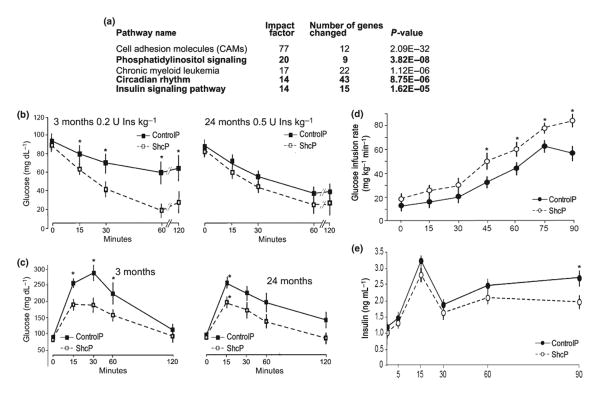
Fig. 1.
ShcP mice have altered insulin-signaling pathways and increased insulin and glucose tolerance. (a) Five hundred top upregulated and five hundred top downregulated genes in different tissues of ShcP KO strain were compared by Onto-Express versus GO database. Resulted list of altered pathways was sorted by ‘Impact Factor’ and the top five presented. (b) For the insulin tolerance test (ITT), ShcP KO mice were challenged with IP injection of insulin at indicated concentration and age of mice. Glucose was measured in blood samples at indicated time points. (c) For the glucose tolerance test (GTT), mice were challenged with injections of glucose. Analogously, concentration of glucose was measured in blood. Ten ControlP and ten ShcP males were used for ITT/GTT experiments. *significant difference, which is p < 0.05 and F > F crit. as obtained by repeated-measurements ANOVA. (d, e) Hyperinsulinemic–euglycemic clamp test on five 3-month-old ControlP and six ShcP male mice. In d, *means p < 0.01, and in e, *means p < 0.05.