FIG. 4.
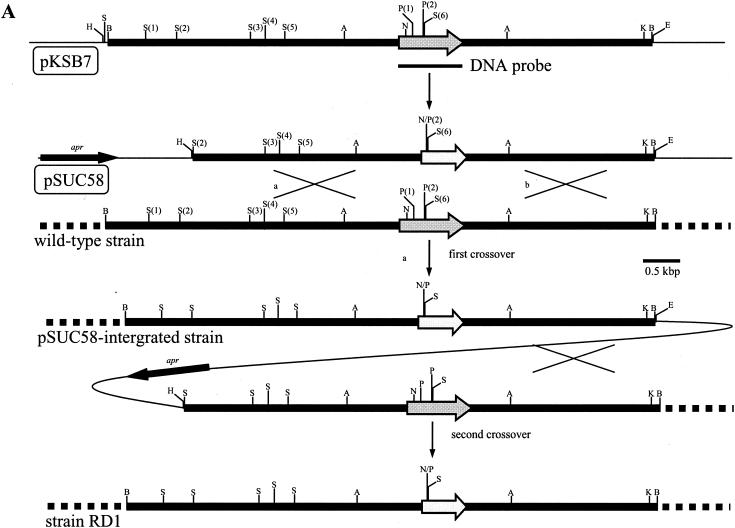
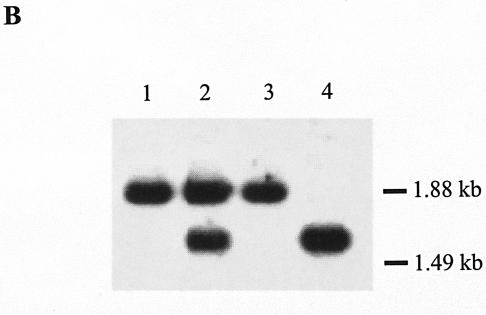
Gene replacement of the K. setae ksbA gene with mutated ksbA by homologous recombination. (A) Schematic representation of the strategy used for the disruption of ksbA. The dark gray arrows indicate the location and orientation of ksbA, and the light gray arrows represent the disrupted ksbA. apr is the apramycin resistance gene. Abbreviations: A, ApaI; B, BamHI; E, EcoRI; H, HindIII; K, KpnI; N, NcoI; P, PstI; S, SalI. For the ApaI sites, two necessary sites among the seven ApaI sites were shown to simplify the map. (B) Southern hybridization analysis of chromosomal DNA from the K. setae wild-type strain (lane 1), pSUC58-integrated strain (lane 2), wild-type segregant (lane 3), and a ksbA disruptant, strain RD1 (lane 4). The probe used was the 0.7-kbp PCR-amplified fragment containing the entire ksbA gene.