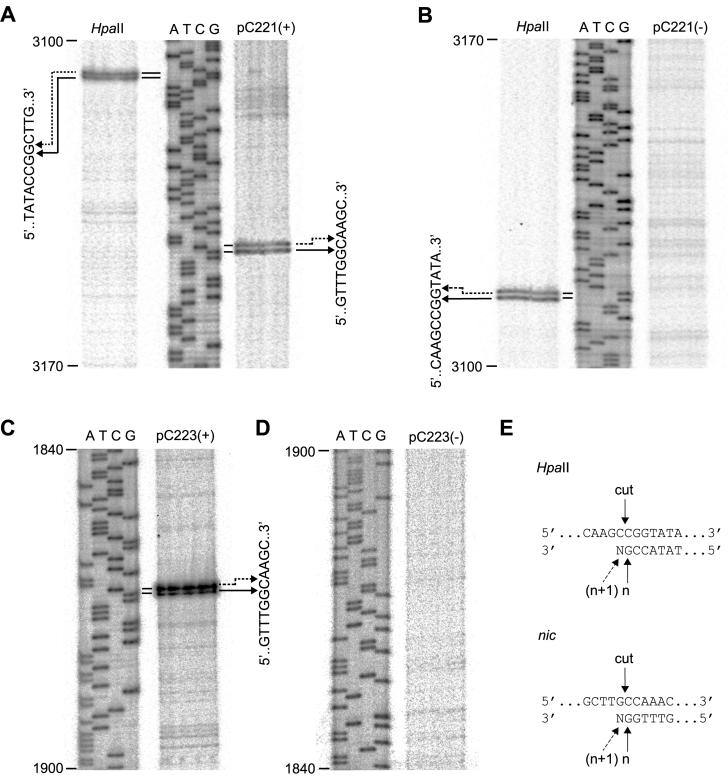
FIG. 4.
Identification of the nic sites of pC221cop903 and pC223. (A) Primer extension analysis against the positive-strand of pC221cop903. The same negative-strand primer was used for all tracks. HpaII, plasmid template cut with HpaII; ATCG, sequencing ladder corresponding to coordinates 3100 to 3170 of the pC221 sequence; pC221(+), pC221cop903 obtained by whole-cell lysate procedure as a template. Doublets resulting from primer extension are correlated with nucleotide sequence by the arrows. (B) Same as for panel A, but with a positive-strand primer. (C and D) Same as for panels A and B, respectively, but with pC223 as a template; this plasmid does not possess a corresponding HpaII site. (E) Interpretation of the primer extension doublets: HpaII cuts the positive-strand as indicated; primer extension products of the expected length (n) and one nucleotide longer (n + 1) are generated by terminal transferase activity of the polymerase. The same interpretation is compatible with a unique nic site at the position indicated.