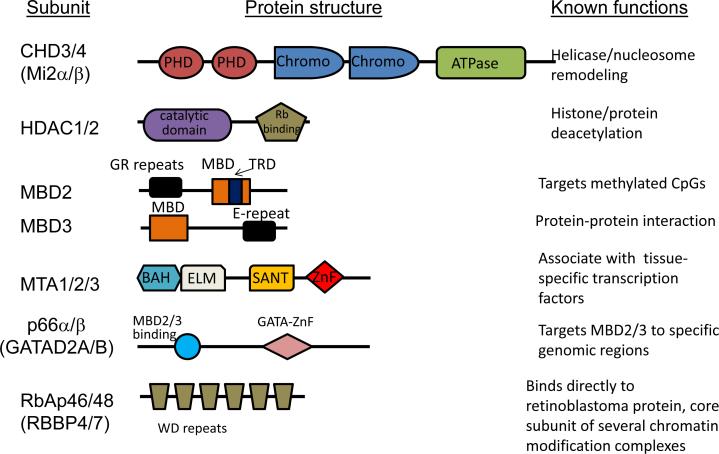
Figure 1. Core components of the NuRD complex.
Conserved protein domains and known functions within the complex are shown for each NuRD subunit and their variants. The CHD3/CHD4 subunit consists of 2 PHD fingers, 2 chromodomains, and an ATPase domain. The PHD fingers are required for interaction with HDAC16 and for modified histone tails96,97. The chromodomains display DNA binding activity and are indispensable for ATPase, nucleosome mobilization, and nucleosome binding98. The ATPase domain carries out ATP hydrolysis which provides the energy necessary for remodeling nucleosome by either histone displacement99,100 or histone octamer sliding101. HDAC1/2 are class I HDACS that share homology to the yeast RPD3 gene and consist of a zinc containing deacetylase catalytic domain. HDAC1 and HDAC2 uniquely contain an additional C terminal Rb binding motif102. MBD2 and MBD3 contain a conserved MBD motif. The MBD domain of MBD2 but not MBD3 binds methylated DNA17,18. MBD2 also contains a glycine and arginine (GR) rich region and a transcriptional repression domain (TRD) involved in recruiting HDAC103,104. MBD3 contains a glutamate (G) repeat region near the C-terminus. MTA1/2/3 share four highly conserved functional domains including the bromo-adjacent homology (BAH) domain, the Egl27/MTA1 (ELM) domain, the SW13, ADA2, N-CoR and TFIII B B” (SANT) domain, and a zinc finger DNA binding domain. The BAH domain is thought to be involved in protein-protein interaction105, while the SANT domain seems to contribute to MTA2-HDAC1 interaction106. The zinc finger domain has been shown to be necessary for interaction with transcription factors or transcriptional co-regulators such as FOG-2107. Function of the ELM domain of MTA proteins remains undefined. p66a/b contain 2 conserved regions. The amino terminal conserved region directly interact with MBD2 or MBD3, while the carboxyl terminal conserved region can interact with histone tails and is important for targeting to specific genomic loci10,13. Both RbAp46 and RbAp48 contain 6 WD-40 repeats which fold into a seven-bladed b propeller structure and binds to histone H4108.