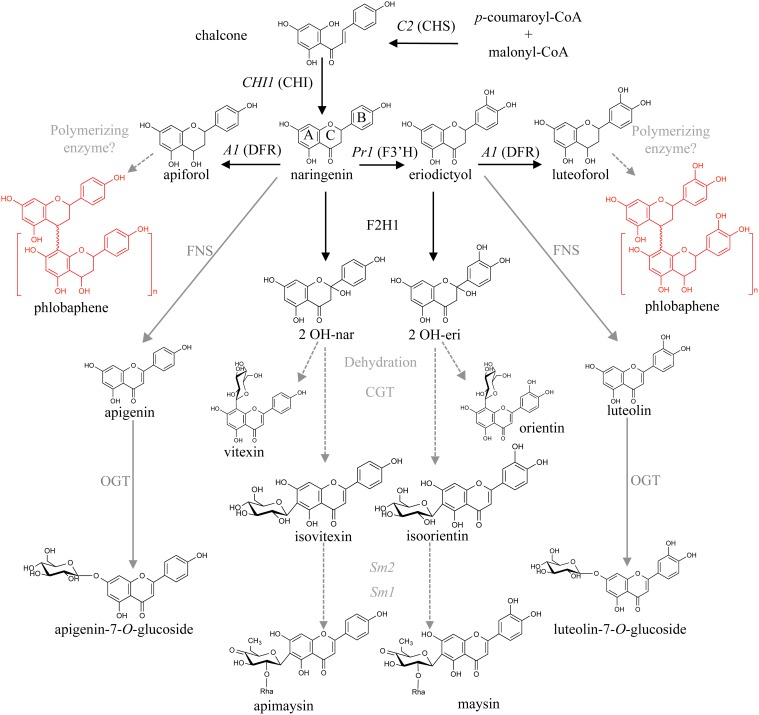
Figure 1.
Proposed maize flavone and 3-deoxy flavonoid biosynthetic pathways. Condensation of p-coumaroyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA by chalcone synthase (referred to as CHS, encoded by the locus C2) results in naringenin chalcone, which is then converted to naringenin by chalcone isomerase (CHI). Naringenin is converted to apiforol (flavan-4-ol) by a dihydroflavonol reductase (DFR, A1) and subsequently polymerized into phlobaphenes. It can also be converted to isovitexin (C-glycosylflavone) by a flavanone-2-hydrohylase (F2H) and a C-glycosyl transferase (CGT). A flavone synthase (FNS) could also catalyze this step followed by an O-glycosyl transferase (OGT). Naringenin can also be converted to eriodictyol by a flavanone-3′-hydroxylase (F3′H, Pr1). The proposed steps for conversion of apigenin and luteolin into the C-glycosylflavones apimaysin and maysin respectively, involve at least three enzymatic conversions: glycosylation at C-6, followed by a rhamnosylation and dehydration steps mediated by the Sm2 and Sm1 loci (adapted from Morohashi et al., 2012). Enzymes identified in black, those proposed in gray.