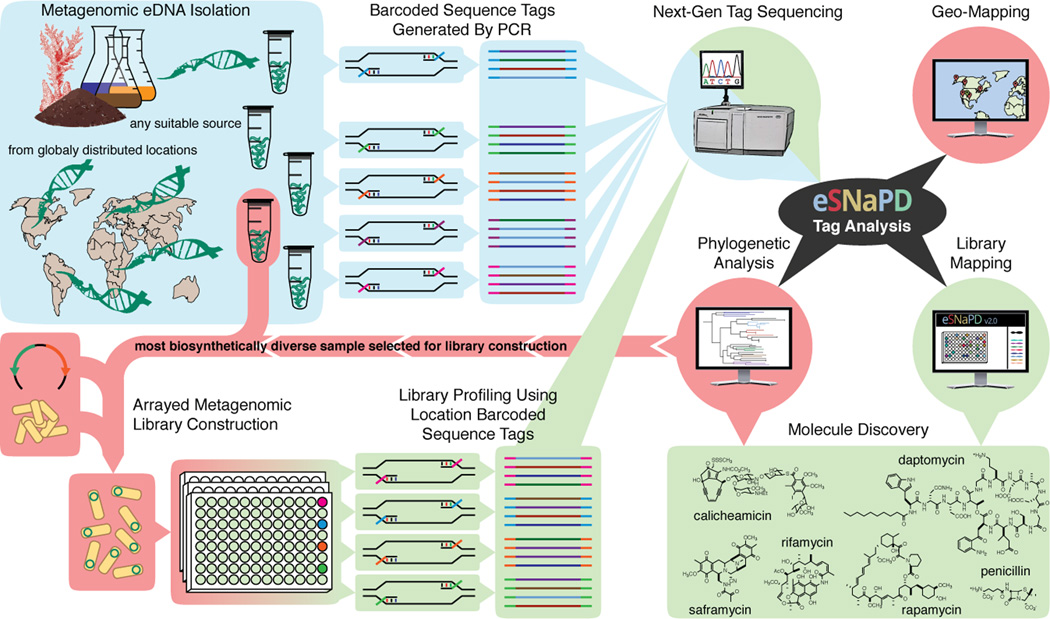
Figure 1.
An overview of eSNaPD assisted small molecule discovery pipeline. Sequence tags are generated by PCR from (meta)genomic DNA isolated from virtually any source using degenerate primers that target conserved biosynthetic domains and can be barcoded to differentiate DNA from different samples in a pooled next generation sequencing run (blue). Raw amplicon sequencing data is processed using eSNaPD bioinformatics platform, which automatically cleans the input data, classifies biosynthetic gene clusters present in the samples by performing a phylogenetic comparison to a reference set of characterized known molecule gene clusters, and visualizes the results in a number of ways that aid in identifying the most desirable samples for library generation (black and red). Newly generated metagenomic library is arrayed, to facilitate identification and recovery of target clones, sequenced using position-specific barcoded primers, and eSNaPD analysis is performed to generate a detailed biosynthetic profile of the library that facilitates the identification of high-value target clones for recovery and heterologous expression (green).