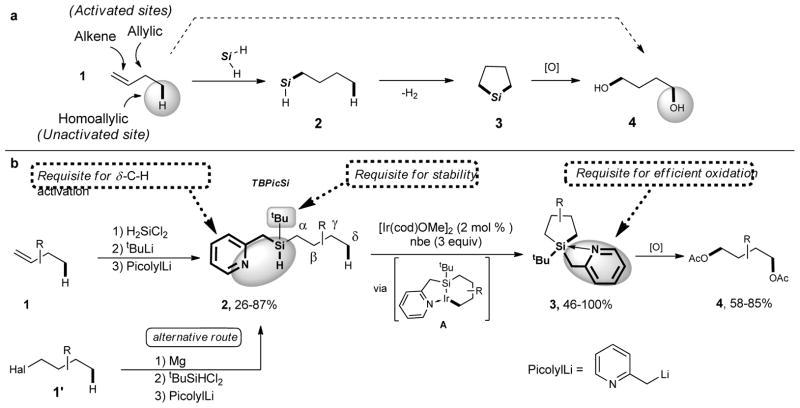
Figure 1. Synthesis of 1,4-diols from 1-alkenes and alkyl halides.
a, General concept for formal 1,4-oxygenation of 1-alkenes 1 into 1,4 diols 4 via activation of homoallylic C–H bond. b, Conversion of 1-alkenes 1 (or 1-haloalkanes 1′) into 1,4-diols 4 via installation of the TBPicSi to form 2, followed by its iridium catalyzed C-H silylation of an unactivated C(sp3)-H bond (to produce the silolane 3), and subsequent oxidation. We designed tert-butylpicolylsilyl (TBPicSi), a new Si,N-type chelating directing group which can be easily installed on alkenes (and alternatively on alkyl halides). Notably, its picolyl moiety enables an efficient Si–H/C–H activation step (via iridacycle A) and, being easily removable from silicon, ensures a successful subsequent oxidation of silolane 3 into the final diol 4. The bulky tert-butyl substituent at silicon is requisite for stability of 2. cod, cyclooctadiene; nbe, norbornene.