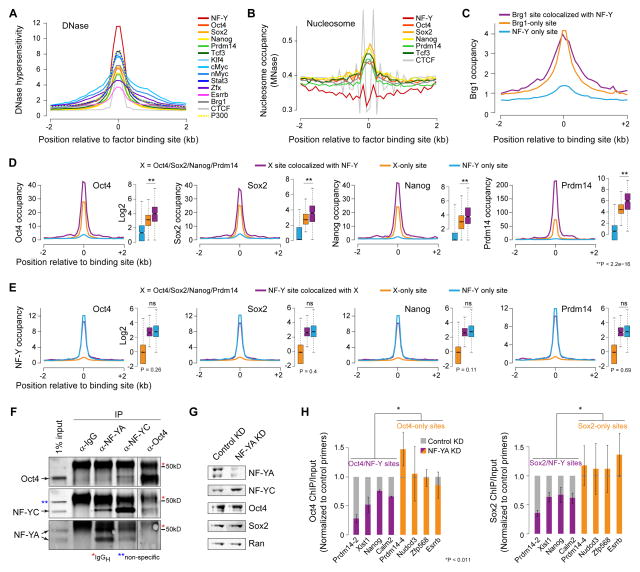
Figure 6. Oct4/Sox2 binding is dependent on NF-Y.
(A) DNase I hypersensitivity, as measured by DNase-Seq (ENCODE, GSE37074), at distal binding sites for various TFs in ESCs.
(B) Nucleosome occupancy, as measured by MNase-Seq (Teif et al., 2012), at distal binding sites for various TFs in ESCs.
(C) Brg1 occupancy at distal Brg1 sites colocalized with NF-Y (purple), distal Brg1-only sites (orange), distal NF-Y sites colocalized with Brg1 (cyan).
(D) Oct4/Sox2/Nanog/Prdm14 (X) occupancy (Ma et al., 2011; Marson et al., 2008) at distal X sites colocalized with NF-Y (purple), distal X-only sites (orange), and distal NF-Y only sites (blue).
(E) NF-Y occupancy at distal NF-Y sites colocalized with X (purple), distal NF-Y only sites (blue), and distal X-only sites (orange).
(F) Co-immunoprecipitation and western blot analysis showing NF-YC and Oct4 co-immunoprecipitating with Oct4 and NF-YC, respectively. As a positive control, NF-YC and NF-YA, two subunits of NF-Y complex, co-immunoprecipitates with NF-YA and NF-YC, respectively.
(G) Western blot analysis of NF-YA, NF-YC, Oct4, and Sox2 in NF-YA KD ESCs 48h after siRNA transfection. Ran used as a loading control.
(H) ChIP-qPCR analysis of sites co-bound by Oct4/Sox2 and NF-Y (purple) or bound by Oct4/Sox2 but not NF-Y (orange) in control or NF-YA KD ESCs. Error bars, SEM. See also Figure S7.