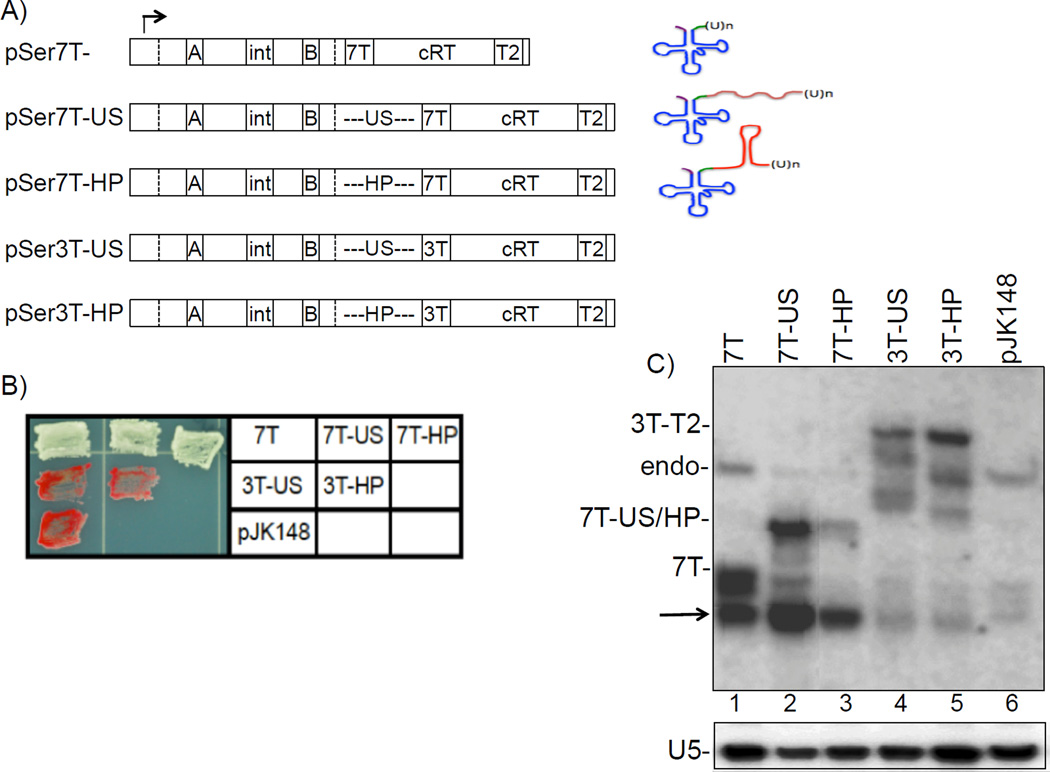
Figure 2. Pol III termination is independent of transcript terminator-proximal RNA structure in vivo.
A) Schematic of the different suppressor tRNA constructs used. pSer7T is the parent construct (8) (see text). Promoter elements and other features are indicated (→, start site; box A; intron; box B; 7T or 3T terminators; cRT, complementary read-through region; T2, read-through terminator). The dashed vertical lines delineate the 5' and 3' matured/processed ends of the tRNA. An unstructured spacer (US) or a spacer that forms a stable hairpin (HP) was introduced within the 3’ trailer, immediately upstream of the terminator. On the right side is a schematic of the resultant predicted pretRNA products. B) Patch suppression assay analysis of S. pombe colonies carrying the different suppressor constructs. Red color indicates lack of suppression and white color indicates efficient suppression. C) Northern blot analysis of the nascent tRNAs produced by the different suppressor constructs using an intron-specific probe. 7T- and 7T-US/HP-designations to the left side indicate the position of the nascent 7T-terminated pre-tRNAs of pSer7T and pSer7T-US/HP constructs respectively. ‘Endo’ indicates the nascent transcript of the endogenous dimeric tRNAser-tRNAi-met gene. 3T-T2- indicates the 3' extended transcript generated by "read through" transcription of the constructs with the 3T terminator. The arrow indicates a partially processed pre-tRNA intermediate prior to nuclear export (see text). The differences in the profiles in lanes 2 and 3 likely reflect alternative 3' processing pathways (15). The lower panel shows the same blot probed for the pol II-transcribed U5 snRNA as a sample recovery control.