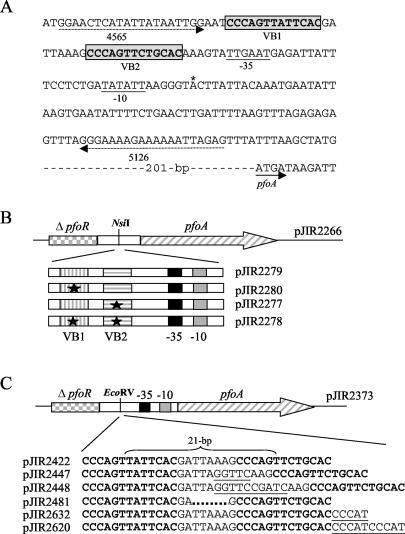
FIG. 1.
Sequence of the VirR binding site upstream of the pfoA gene and analysis of mutated VirR boxes. (A) The VirR boxes, labeled VB1 and VB2, are enclosed in gray boxes, and their sequences are shown in bold. The −35 and −10 boxes of the pfoA promoter are underlined, the transcription start point is indicated by an asterisk, and the start of the pfoA gene is indicated by a solid arrow. The locations of the oligonucleotide primers (4565 and 5126) used to amplify the DNA targets for the gel mobility shift assays are indicated by dashed arrows. (B) Cloning of mutated VirR boxes into pJIR2266. Inserts containing the wild-type VirR boxes or the various VirR box mutations were amplified with primers 14347 and 14348. The resultant PCR products were then cloned into the unique NsiI site in pJIR2266. This vector contains the pfoA gene (hatched arrow) and the 3′ end of the pfoR gene (checked rectangle). Each of the inserts harbored the −10 and −35 boxes, which are represented by gray and black boxes, respectively. The VirR boxes are shown as rectangles with vertical or horizontal stripes. The black stars indicate the mutated boxes, and the resultant plasmids are indicated to the right of each insert. (C) Cloning of VirR box cassettes into pJIR2373. Annealed complementary oligonucleotides containing the wild-type or mutated VirR boxes were inserted into the unique EcoRV site of pJIR2373. This vector contains the pfoA gene (hatched arrow), the −10 box (gray box), the −35 box (black box), and a truncated pfoR gene (checked rectangle). The VirR box sequences are shown in bold, while the inserted nucleotides are underlined. The deletion in the intervening region is indicated by dots. The resultant plasmids are shown to the left of each insert. The 21 bp separating the centers of the VirR boxes are indicated by a brace.