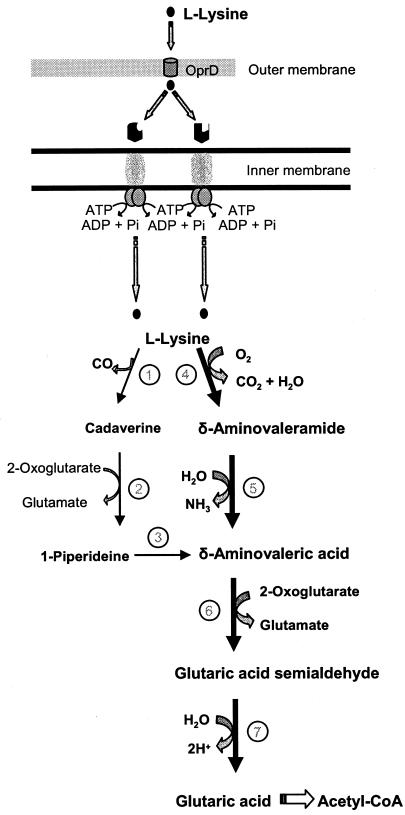
FIG. 1.
l-Lysine catabolism by P. putida. l-Lysine has been proposed to enter into the periplasmic space through the OprD porin (43). Subsequently, it is transported to the cytoplasm (the present study) and is metabolized through two branches that converge at δ-aminovaleric acid (12, 35). Further metabolism of δ-aminovaleric acid yields glutaric acid that is channeled to Krebs cycle intermediates. The thick arrows indicate the main catabolic pathway (Revelles, unpublished). The enzymatic steps are indicated as follows: 1, l-lysine decarboxylase; 2, cadaverine aminotransferase; 3, 1-piperideine dehydrogenase; 4, l-lysine monooxygenase; 5, 5-aminovaleramide amidase; 6, 5-aminovalerate aminotransferase; 7, glutarate semialdehyde dehydrogenase.