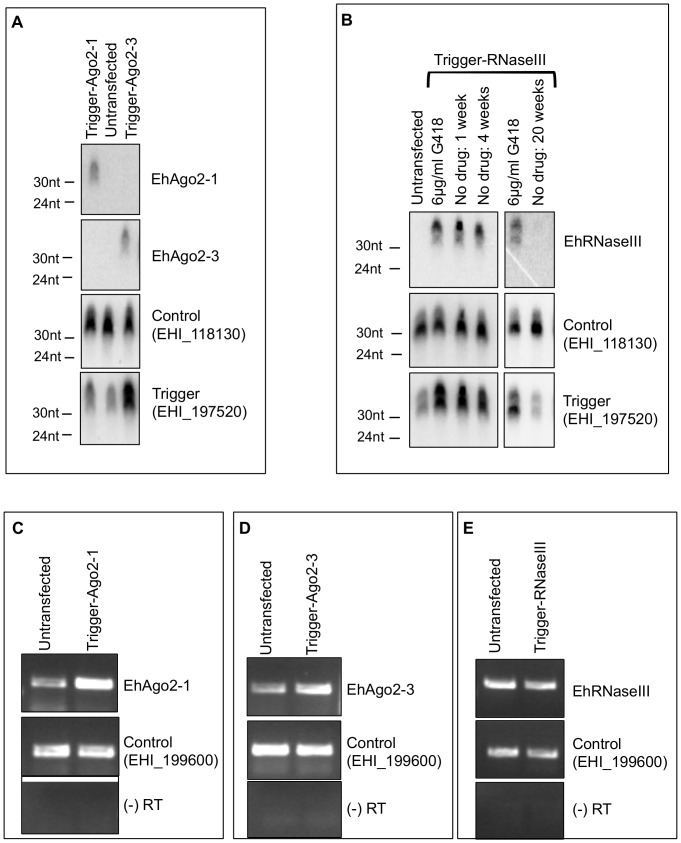
Figure 2. Antisense sRNAs are detected to putative RNAi genes but do not silence the target genes.
(A) High resolution Northern blot of parasites transfected with the trigger-EhAgo2-1 or the trigger-EhAgo2-3 plasmid. Cell lines maintained at 24 µg/ml G418. Gene-specific AS sRNAs to Ago2-1 or Ago2-3 are detected in the respective cell lines. AS sRNAs to EHI_188130 (loading control) and EHI_197520 (trigger) serve as controls. (B) High resolution Northern blot analysis of trigger-EhRNaseIII transfectants maintained in 6 µg/ml G418 or removed from drug selection for 1, 4, or 20 weeks. Abundant EhRNaseIII AS sRNAs are detected at all time points excluding the 20-week removal from drug sample. The 20-week sample shows a very faint population of EhRNaseIII AS sRNAs. Controls are the same as in (A). (C) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR of trigger-EhAgo2-1 transfectants at 24 µg/ml G418 shows an increase in EhAgo2-1 transcript abundance compared to untransfected cells. EHI_199600 was used as a loading control and -RT samples as negative controls. (D) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR shows an upregulation of EhAgo2-3 transcript in the trigger-EhAgo2-3 cell line at 24 µg/ml G418 compared to untransfected cells. Controls are the same as in (C). (E) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR of trigger-EhRNaseIII transfectants at 6 µg/ml G418 shows that the abundance of EhRNaseIII transcript is unaffected by the presence of gene-specific AS sRNAs. Controls are the same as in (C).