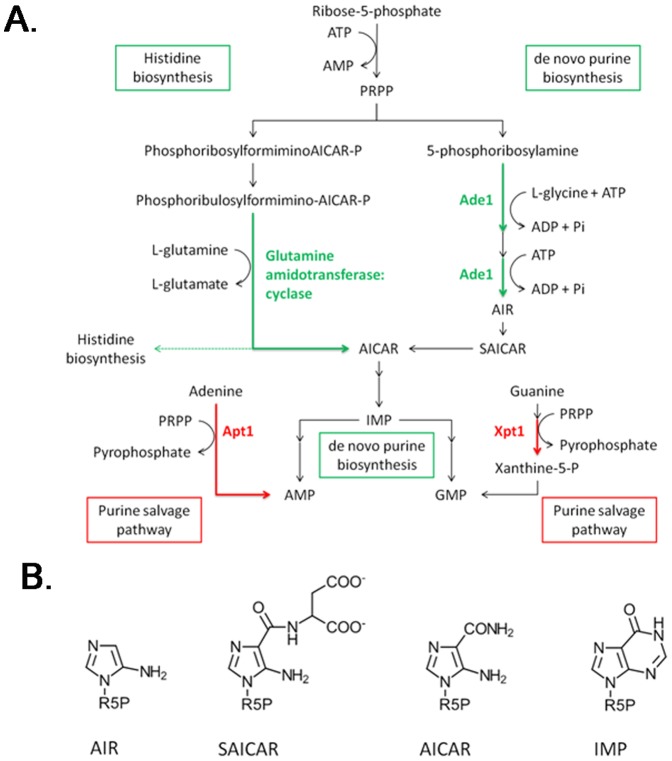
Figure 4. Overview of the regulation of the purine metabolic pathway by gliotoxin and H2O2, either alone or in combination.
(a) Purine-related enzymes and pathways undergoing an increase in expression, relative to the solvent control, are indicated in red and decreased expression is indicated in green. Metabolites are indicated in black. Ade1, bifunctional purine biosynthetic protein; Xpt1, xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase; Apt1, adenine phosphoribosyltransferase. Enzymes of the histidine and de novo purine biosythesis converging pathways, glutamine amidotransferase: cyclase and Ade1, are down-regulated in response to gliotoxin. Expression of enzymes involved in the purine salvage pathways, Xpt1 and Apt1, is up-regulated in the presence of H2O2 and gliotoxin, repsectively, relative to a solvent control [20], [23]. Figure adapted from pathway.yeastgenome.org. (b) Structures of intermediate molecules in the purine and histidine biosynthesis pathway; 5-aminoimidazole ribonucleotide (AIR), N-succinyl-5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide (SAICAR), 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide (AICAR) and inosine monophosphate (IMP). R5P = ribulose-5-phosphate.