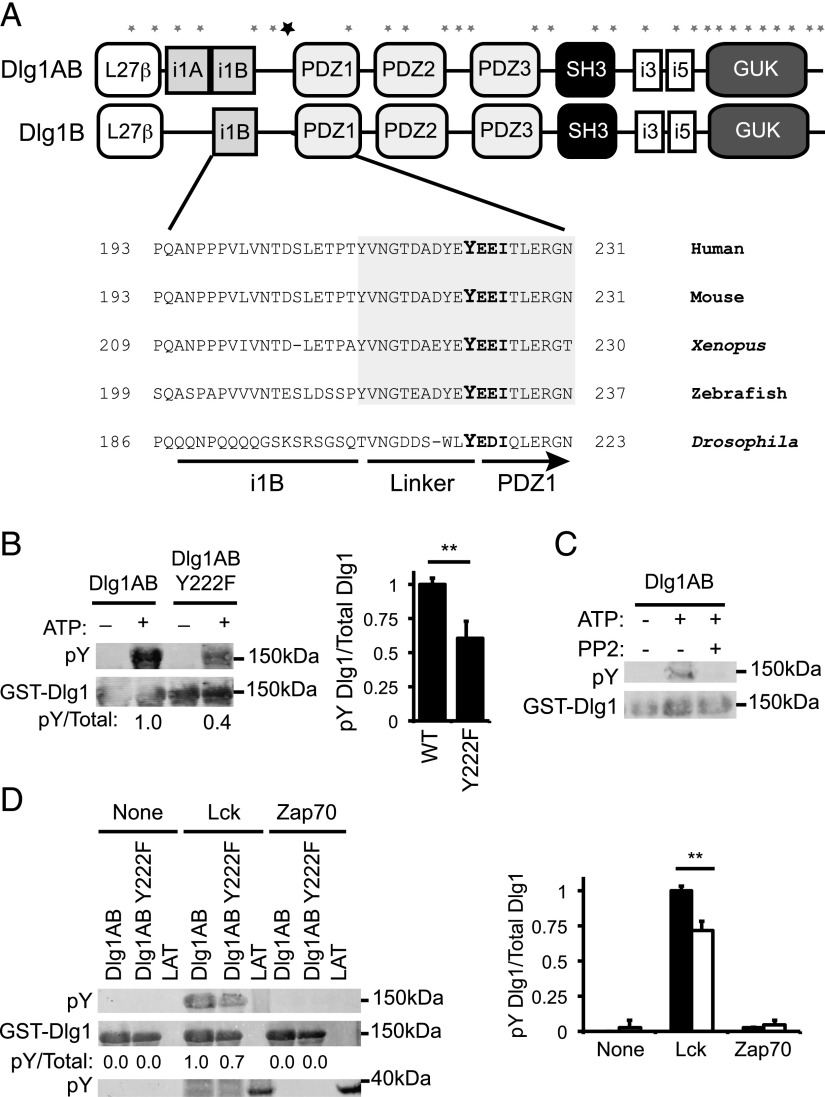
FIGURE 2.
Dlg1-associated Lck phosphorylates Dlg1 at position tyrosine 222. (A) Domain structure of Dlg1AB and Dlg1B. Asterisks indicate the location of the 29 tyrosine residues along the Dlg1 sequence. The bold asterisk indicates the location of Y222. (A, bottom inset) Amino acid sequence alignment of the region of Dlg1 surrounding Y222 from various all species listed in the National Center for Biotechnology Information Database. Shaded region indicates evolutionarily conserved linker region of Dlg1. (B) In vitro kinase assays using GST-Dlg1AB WT or GST-Dlg1 Y222F (Tyr to Phe mutation) fusion proteins bound to glutathione–Sepharose beads and incubated with T cell lysates, centrifuged, washed, and incubated with ATP. Protein complexes subjected SDS-PAGE and blotted using anti-4G10 (pY-Dlg1) and anti-GST (GST-Dlg1). (C) In vitro kinase assay using GST-Dlg1AB fusion proteins bound to glutathione–Sepharose beads and incubated with T cell lysates, centrifuged, washed, and incubated with ATP in the presence or absence of 10 μM PP2 inhibitor. Protein complexes were subjected SDS-PAGE and blotted using anti-4G10 (pY-Dlg1) and anti-GST (GST-Dlg1). (D) GST-Dlg1AB WT or Y222F fusion proteins were bound to glutathione–Sepharose beads and incubated with ATP and rLck, rZap70, or buffer only (none). Proteins were subjected to SDS-PAGE and blotted for anti-4G10 (pY-GST-Dlg1 and pY-GST-LAT) or anti-GST (GST-Dlg1). (B, right; D, right) Blots were quantitated using Li-Cor Odyssey software. pY-Dlg1 was normalized to total Dlg1 for each lane, and WT phosphorylation was set to 1.0; error bars represent the SD of four independent experiments. **p < 0.05.