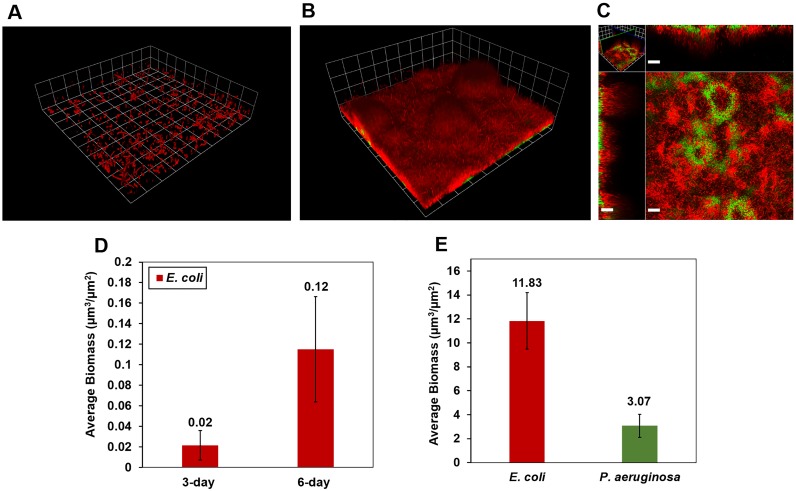
Figure 7. Colonization of E. coli biofilms by P. aeruginosa in R2A medium.
E. coli appears red and P. aeruginosa-GFP appears green or yellow. A) After 3-days of mono-species growth, E. coli formed sparse biofilms composed of small, isolated cell clusters (grid unit is 23.8 µm). B) Mixed P. aeruginosa and E. coli biofilm on day 6, after 3 days of mono-species E. coli growth plus 3 additional days of multi-species growth after inoculation of P. aeruginosa. (grid unit in B is 23.8 µm). Following introduction of P. aeruginosa, E. coli grew prolifically and adopted a configuration similar to that observed in other mixed-species experiments. C) Horizontal section near the base of the biofilm and vertical sections of the biofilm shown in panel B (scale bar = 20 µm). D) Biomass of 3-day- and 6-day-old E. coli mono-cultured biofilms. E) Biomass of co-developed biofilms after 3 days of E. coli growth plus 3 additional days of multi-species growth after inoculation of P. aeruginosa.