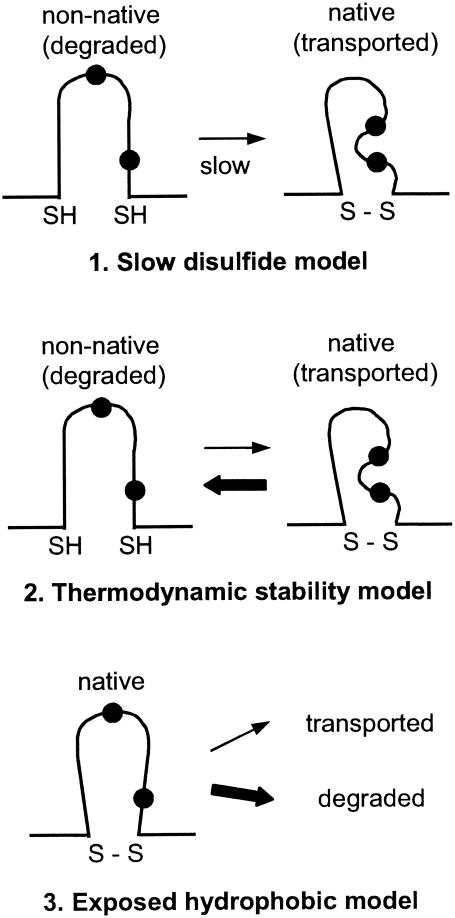
FIG. 7.
Models of p10 degradation. Three possible models to explain the influence of the p10 ectodomain and the HP on p10 degradation by the ERAD pathway are shown. The first model implies that the slow formation of an intramolecular disulfide bond (S—S) leads to exposed thiol (SH) or hydrophobic residues (filled circles) in the nonnative structure which target p10 for degradation. The second model implies that it is not the rate of folding of the p10 ectodomain but rather a low thermodynamic stability of the native structure that leads to transient and repeated exposure of thiol or hydrophobic residues. The third model implies that hydrophobic residues are naturally surface exposed in the native p10 ectodomain structure, leading to recognition and degradation of the majority of p10.