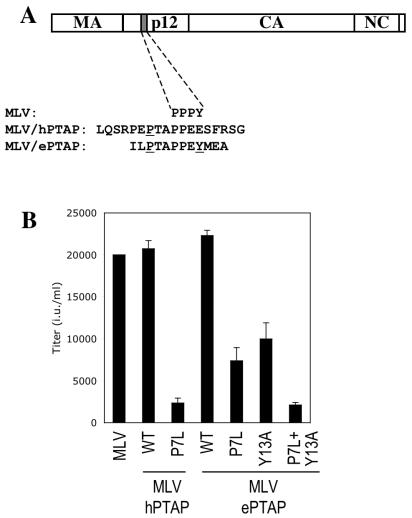
FIG. 2.
L-domain activity of PTAP and PPXY motifs from the EbVP40 L domain in the context of MLV Gag. (A) Schematic representation of the MLV/hPTAP and MLV/ePTAP proviral constructs. The endogenous PPPY motif in MLV is replaced by residues from the HIV-1 PTAP L domain or the EbVP40 L domain, as indicated. Residues that were mutated in these constructs are underlined. In both cases P7L refers to the first proline residue in the PTAP motif. Coincidentally, this residue is the seventh residue from the N terminus of both HIV-1 p6 and EbVP40. (B) Effect of mutations in the transplanted HIV-1 and EbVP40 L domains on MLV virion formation. Infectious virus production by cells transfected with a GFP-expressing MLV vector, a vesicular stomatitis virus G expression vector, and the indicated wild-type (WT) or mutant MLV/hPTAP or MLV/ePTAP proviral plasmids. Infectious virions were measured by flow cytometry analysis of cells inoculated with culture supernatants and are given in infectious units (i.u.).