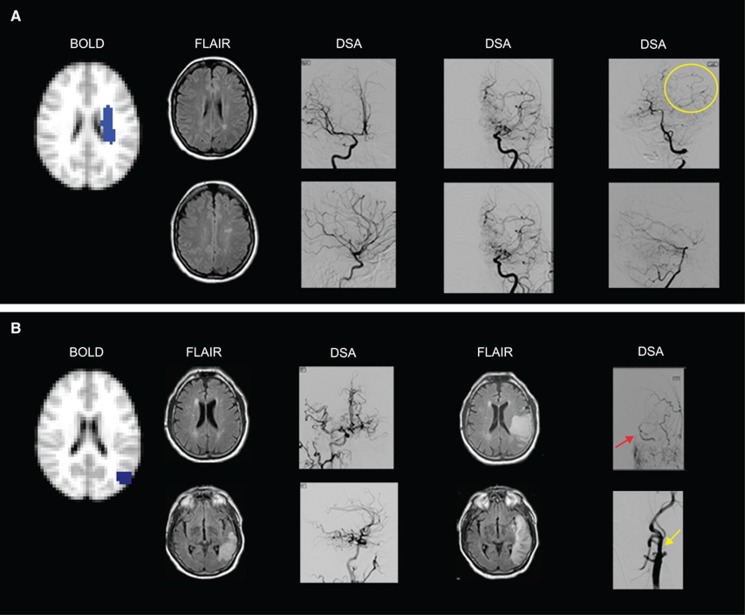
Figure 6.
(A) Negative cerebrovascular reactivity (CVR) as a result of vascular steal is seen in the left centrum semiovale of a 25–year-old female with moyamoya disease. Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) images show remote infarcts in the watershed distribution of the left hemisphere. Anterior–posterior (AP) and lateral projections from digital subtraction angiography (DSA) performed 1 week before hemodynamic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) show (left DSA image) mild stenosis around the carotid bifurcation with slightly developed internal carotid artery (ICA) moyamoya (modified Suzuki score, mSS I) on the right after right ICA injection, (middle DSA image) occlusion of both the anterior cerebral artery and middle cerebral artery with well-developed ICA moyamoya (mSS III) on left external carotid artery (ECA) injection, and (right DSA image) extensive leptomeningeal collaterals from the posterior circulation to the anterior circulation upon left vertebral injection (yellow circle). (B) Negative CVR with increased cerebral blood flow in the left parietal cortex in a 72-year-old male with atherosclerotic intracranial disease. Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery images (left FLAIR image) at the time of hemodynamic MRI show a left posterior temporal–occipital infarct inferior to the region with negative reactivity (participant presented with acute aphasia 2 days before hemodynamic MRI). Anterior–posterior and lateral projection from DSA after right common carotid artery (CCA) injection shows (left DSA image) extensive cross-filling of the left cerebral hemisphere via the anterior communicating artery. Eight days later, FLAIR images (right FLAIR image) from a second MRI show the progression of the infarct to the region of negative CVR. The participant's aphasia had worsened with stroke extension that occurred when his blood pressure fell at a rehabilitation facility, 4 days after hemodynamic MRI. Anterior–posterior projections from left CCA injections show (right DSA image) collateral flow from the ECA to the intracranial ICA (red arrow) distal to the occluded cervical ICA stump (yellow arrow).