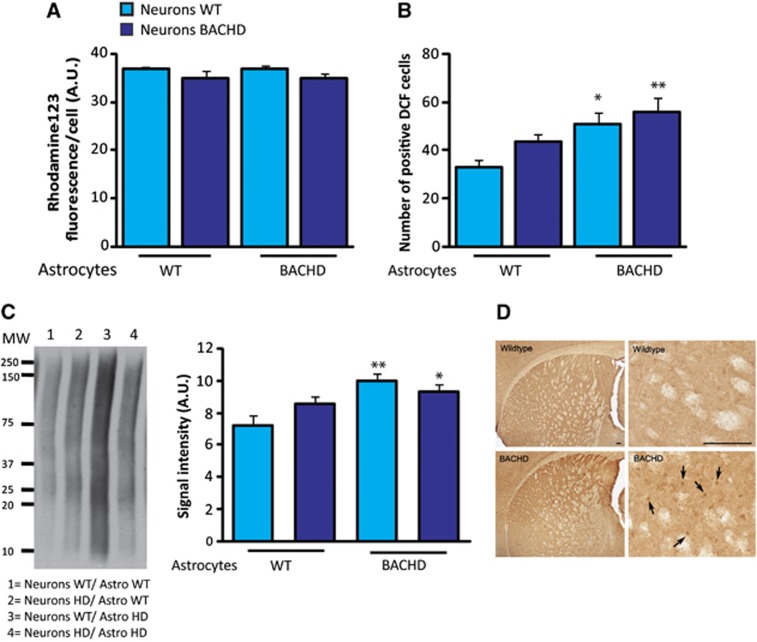
Figure 7.
Astrocytic mHtt increases oxidative stress in neurons. (A) The mitochondrial membrane potential is not affected by the expression of mHtt in neurons as assessed using Rhodamine 123 staining in living neurons (neurons WT/astrocytes WT n=5, neurons HD/astrocytes WT n=5, neurons WT/astrocytes HD n=7, neurons HD/astrocytes HD n=8; (two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA, neuron genotype), F(1,21)=1.10; P=0.31; (astrocyte genotype), F(1,21)=1.80; P=0.19). (B) A significant increase in ROS production was observed in BACHD neurons and WT neurons cultured with BACHD astrocytes using 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (H2DCFDA), a cell-permeant indicator for ROS (two-way ANOVA (astrocyte genotype), F(1,28)=11.75; P=0.0019) whereas neurons genotype did not affect oxidative stress (two-way ANOVA (neuron genotype), F(1,28)=2.92; P=0.098) (neurons WT/astrocytes WT n=7, neurons HD/astrocytes WT n=7, neurons WT/astrocytes HD n=8, neurons HD/astrocytes HD n=8). (C) Immunoblot of carbonyl adduct formation shows an increased expression of carbonyl residues of neuronal proteins only when neurons are cultured in the presence of HD astrocytes (n=4 per condition, two-way ANOVA (neuron genotype), F(1,12)=0.36; P=0.57; (astrocyte genotype), F(1,12)=11.84; P=0.0049). Immunostaining of 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine (8-OH-dG) is increased in the dorsal striatum of 12-month-old BACHD mice (arrow) compared with WT mice (D) (n=3 per genotype). All data represent means±s.e.m. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 compared with WT/WT condition. a.u., arbitrary unit; DCF, 2',7'-dichlorofluorescein; HD, Huntington's disease; ROS, reactive oxygen species; WT, wild-type.