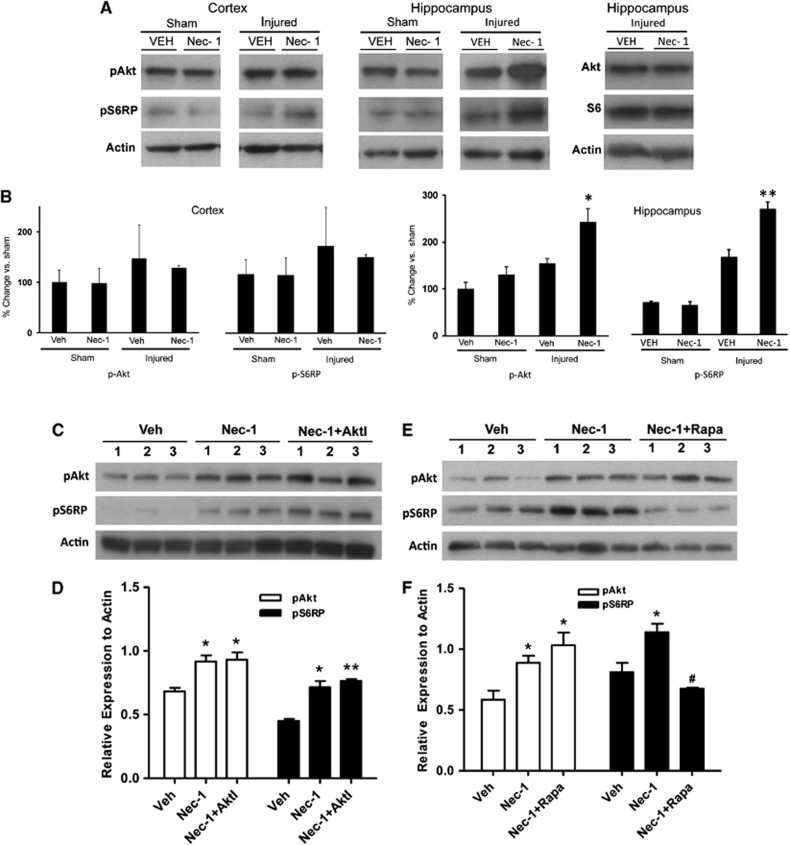
Figure 6.
Necrostatin-1 administration increases Akt (protein kinase B) and S6 phosphorylation after closed head injury (CHI). (A) Administration of necrostatin-1 (Nec-1) before CHI had no effect on Akt or S6 phosphorylation in the cortex in sham or CHI mice, but pretreatment with Nec-1 increased phosphorylation of Akt-473 and S6RP in hippocampal brain homogenates at 24 hours after CHI. After CHI, Nec-1 administration did not increase total Akt (P=0.96, n=3/group) or total S6 (P=0.83 versus Veh, n=5–6/group) in the hippocampus. (B) Densitometric analyses of western blot data of the phosphoproteins shown in A. *P<0.01 versus injured, Vehicle (Veh; n=4/group); **P<0.005 versus injured, Veh (n=4/group). (C) Co-administration of Nec-1 and Akt inhibitor viii (AktI) did not prevent the increase in hippocampal p-Akt 473 or p-S6RP observed with Nec-1 alone. (D) Within-group densitometric analyses of the western blot data in C (*P<0.05 versus Veh; **P<0.01 versus Veh, n=3/group). (E) Compared with vehicle, treatment with Nec-1 increased phosphorylation of hippocampal Akt-473 and S6RP, whereas co-administration of Nec-1 and Rapa prevented the increase in p-S6RP observed with Nec-1 alone. (F) Densitometric analyses of western blot data in E. *P<0.05 versus Veh; #P<0.05 versus Nec-1 treatment (n=3/group).